Turkey Eyeing Further Expansion in Northern Syria, Say Rebels
Turkey said last week that its campaign in Idlib was nearly complete, but recent talk over further expansion in Aleppo’s countryside signal that its operations in northern Syria may be far from over.

A map of control in northeast Syria, showing front lines between the opposition, Kurdish forces and the Syrian government. By Omran Center -Nawar Oliver
After establishing a presence in northern Idlib and western Aleppo over the past month, Turkish troops and Turkey-backed rebels are now looking to expand their area of control along the border by moving further east into Aleppo’s countryside, a rebel spokesman told Syria Deeply.
Although Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdogan said last week that his country’s operation in northeast Syria was nearly complete, Ankara recently dispatched reconnaissance teams to new areas, and some rebels reported being in talks to hand over their positions to Turkish forces, according to a military spokesman for the Syrian opposition faction Nour al-Din al-Zenki.
Ankara began its cross-border operation with the purported aim of enforcing a de-escalation zone in Idlib, which was agreed upon by Russia, Turkey and Iran in the Kazakh capital of Astana in September. So far, its troops have deployed only in areas separating the opposition and Kurdish forces. The Turks have not moved into front-line areas between rebels and the Syrian regime.
According to Abdul Salam Abdul Razzaq, Turkey is looking to replicate this strategy further east. He told Syria Deeply that Nour al-Din al-Zenki had already agreed to hand over its positions in rural Aleppo to Turkish forces.
He added that although it had not been determined exactly where the Turkish troops would be stationed, Ankara was looking to establish observation posts in the Sheikh Aqil Mountains, located in the al-Bab district, which Turkey liberated from the so-called Islamic State last year.
Ankara has also dispatched reconnaissance teams to Nour al-Din al-Zenki positions in the adjacent districts of al-Tamoura and Anadan, northwest of Aleppo city, but had not yet taken them over, Abdul Razzaq said. The military spokesman also cautioned the agreement could fall through if Aleppo residents objected to the Turkish presence.
It was not immediately clear what Nour al-Din al-Zenki stands to gain from the agreement. “Turkey’s deployment in Idlib is part of the de-escalation zone agreement reached in Astana, and Zenki is a signatory to this deal,” Abdul Razzaq simply said.
When asked about the significance of these positions, Abdul Razzaq said they were a clear indicator of Turkey’s attempts to encircle the Kurdish-held region of Afrin. “If the Turkish army’s priority was ensuring de-escalation, then Ankara should have first deployed on the front lines between the opposition and the regime, instead of on the front lines with Kurdish separationists,” he said. “Everyone knows that Kurdish forces are Ankara’s greatest concern when it comes to its southern borders.”
Speaking to his ruling Justice and Development Party (AKP) last month, Erdogan said that although Turkey’s Idlib operation was nearly complete, “the Afrin issue is ahead of us … We can come suddenly at night. We can suddenly hit at night.”
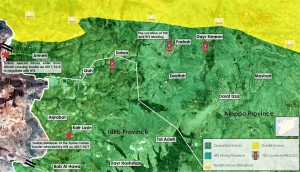
Turkish Deployment in Northeast Syria

A map showing Turkish positions in Idlib province as well as front lines between Turkish forces and Kurdish groups based in the adjacent Kurdish-held region of Afrin. By Omran Center-(Nawar Oliver)
Turkey’s planned expansion comes after weeks of operations in northern Idlib and western Aleppo that have resulted in the establishment of at least three Turkish posts in areas adjacent to the Kurdish-held region of Afrin.
Omar Khattab, a military spokesman for the Turkey-backed Ahrar al-Sham rebel group, said that Turkish deployment in Idlib has been carried out in coordination with the al-Qaida-linked Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham alliance, which withdrew from areas of Turkish operations.
Charles Lister, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute, told Syria Deeply last month that HTS agreed to surrender positions to the Turkish army to prevent a costly all-out war with Turkish troops.
Ahrar al-Sham’s military spokesman said he was not authorized to disclose the exact coordinates of these positions, but Ahmad Saoud of the Free Idlib Army’s Division 13 Brigade said Turkey has built a launching-pad base in the Sheikh Barakat Mountain in Dar Simeon.
The position is only a few miles from Kurdish militia forces based in Jendaris and is located roughly 7 miles (12km) from the Turkish borders. A video posted by the activist-run Smart News Agency on October 24 shows Turkish bulldozers and armored vehicles operating in the area.
Turkish troops have also dispatched forces to the village of Salwa, which is near the border of Afrin, according to Abdul Razzaq. The activist-run Thiqa News Agency has posted a video on social media networks showing Turkish armored vehicles moving in the area.
Rebel sources said that Turkish troops have also purportedly deployed in the village of Fadrah near the Sheikh Barakat Mountain.
Turkey’s operations in northern Syria are laying the groundwork for the establishment of a border buffer zone that stretches from the Atmeh border crossing as far east as Jarablus. Following the Euphrates Shield Operation last year, Turkish-backed forces gained control over the Jarablus, Azaz and al-Bab in Aleppo’s countryside. Current expansion in Anadan, Tammoura and Sheikh Aqil will help Turkey connect its positions in Northern Idlib with Euphrates Shield territory in Aleppo’s countryside.
In another indication of Ankara seeking to entrench itself along this stretch of the border, Turkey’s state-run Anadolu news agency reported last week that Turkey has reportedly trained some 5,632 Syrian volunteers to work as police officers in the area. Some volunteers have already been dispatched to the areas of al-Bab, Azaz and Jarablus, Anadolu said.