Articles
Briefing on Latest Developments in Idlib
I. Introduction
Both Turkey and Russia agreed to a ceasefire in Idlib starting at midnight on March 5th,2020. At the time, both sides saw this agreement as representing the least worst case scenario to preserve its interests on the ground and prevent further escalation between different actors. On one side, the Russians and regime forces heavily escalated systematic attacks on civilians and basic infrastructures driving over 1.1 million civilians towards the Turkish borders, hence putting pressure on Turkey and indirectly on Europe. The regime aided by the Russian airforce regained control over vacated villages in the Idlib province and was advancing on more heavily populated areas. On the other hand, after several attacks by the regime against Turkish military forces, the Turkish army heavily escalated its presence and equipment in southern Idlib and broke away with previously agreed “rules of engagement” by attacking regime and Iranian backed forces to stop its advance and prevent further displacement of the civilian population. The agreement hence, was a temporary freeze of operations by all sides. It included the following core elements:
• A ceasefire from the morning of March 6, 2020 along the frontline.
Regime artillery continued to target several locations in the vicinity of the new buffer zone north of the M4, Sources confirmed that 56 violations done by the Regime March 6 to March 31 of the same month.
• Establishing a security corridor six kilometers north and six kilometers south of the main international highway in Idlib "M4," which links the cities controlled by the Syrian Regime in Aleppo and Lattakia, and open an internal crossing between the Regime and Opposition held areas.
Because of the new Corona (COVID19) and the fear of an outbreak of the disease, the interm government in Idlib decided to close all the internal and external borders in Idlib and western Aleppo, but in April 17, 2020 HTS announced its intention to open a commercial crossing with the regime that links both Saraqib and Sarmin, which met with widespread disapproval among civilians and demonstrated near Sarmin objecting to the matter.
• Joint Russian-Turkish patrols to be deployed along the M4 road, starting March 15.
As of April 18, 2020, no full joint patrols were conducted for the entire route for security and logistical reasons. A group of civilians built tents along parts of the road, refusing the passage of Russian patrols, while some military factions took advantage of the situation and worked to further destabilize the security situation. Sources of the Information Unit at Omran Center confirmed that these factions are affiliated with HTS. HTS has been taking steps to indirectly create problems and then present itself as part of the solution in an attempt to legitimize its presence in any future security architecture.
II. Updated map of control in Idlib and its surrounding areas
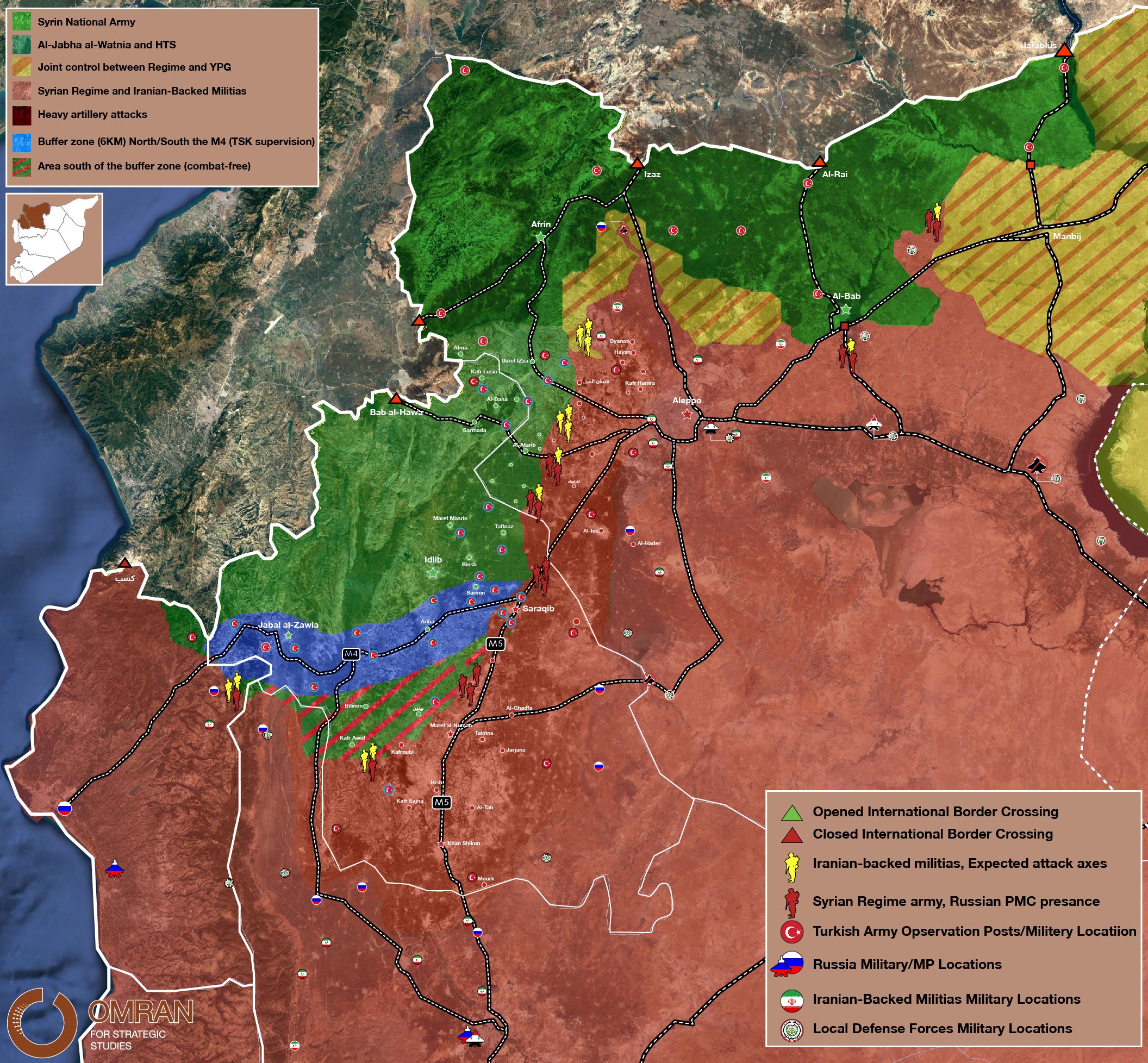
Updated Control map of Control in Idlib by Information Unit in Omran Centre – 18 April 2020
III. Major developments of the "M4" agreement
A. Turkey’s four current goals
1. Preventing the threat of Corona (COVID19) especially in IDP camps. This can be observed through the strict measures at border crossings, reducing to the maximum interactions with locals, pushing IHH organization to improve its plans, as well as high engagement by AFAD.
2. Increasing Turkish Military posts defense and sending more vehicles and soldiers in the past weeks to establish new posts in Jabal al-Zawyie and al-Ghab Plain.
3. Opposition factions: restructuring National Liberation Front (NLF) by arresting and demoting corrupt commanders, requesting from each faction to call fighters to training camps to compare numbers of fighters and ending any possible connection between groups and other countries in order to ensure order and containment.
4. The M4 agreement with Russia: Turkey is pushing hard for the joint patrols on M4, which has been facing obstacles through sit-in demonstrations by some local actors with direct threats from HTS sub-entities. Turkey is carefully trying to end this situation without using force and by negotiating with the locals. Resolving this situation is a top priority before May in order to prevent any Russian military acts.
B. Positions of local and international actors in Idlib
1. The joint patrols along the M4 highway is Russia’s main priority. There were little if any statements by Russia calling upon Turkey to implement the agreement during February-April, unlike early January. Russia is focusing on dealing with the Corona pandemic and countering increased ISIS threats in eastern Homs, Daraa, and Deir Ezzor.
2. Several news sources indicated that the UAE is pushing the regime to launch a new attack on Idlib and giving promises to fund such an operation. Russia asked the regime not to launch any attack after regime unilaterally and without consulting the Russians sent reinforcements to Idlib.
3. The presence of Iranian-backed militias in Idlib is less than other areas in Syria. However, for Iran to establish a foothold it needs to send more fighters and to launch a limited attack. IRGC-affiliated militias are present in Kafrnabel but are not the main attacking force. Once again, Iran is using its old methods: initial expansion in new areas followed by provision of basic services for local communities.
4. The recent Turkish/Russian agreement put further pressure on HTS by pushing it to re-share power in Idlib with NLF. Furthermore, the Turkish heavy military presence and the deal with the Russians is making Jihadist inside HTS angry and pushing them to breakout. This can be seen in the resignation of Abu Malek al-Talli, and the sit-in protests on the M4 by offshoot members of HTS.
5. HTS has been taking steps to restructure itself, and started by forming 3 new divisions and mixing the hardcore jihadist groups with other less radical members under the leadership of local members.
6. HTS seems to attempts to contain and weaken the more extreme elements within its ranks in order to reduce the risks of possible defections and ensure a future smooth transition from a Jihadi group to a political Islamist group. It is also taking steps to continue its local control over governing bodies such as the Salvation Government.
IV. Future directions
1. There will most likely not be a major regime attack in the near future and even from the opposition side too.
2. May is the month of action for the Turkish sides in order to get ready of the difficult situation surroundings the M4 agreement.
3. The area is witnessing more Iranian-backed militias activities, those activities will increase I. The future in different levels (Economic, Security and military)
4. COVID19 is not the main concern for the local and international actors in Idlib; positive reading is confirmed from the Opposition held areas in Idlib.
Control and Influence Changes After Operation "Peace Spring"
This report examines, in numbers and charts, the developments in the northern region of Syria after the commencement of operation “Peace Spring" by the Turkish military and the Syrian National Army (SNA). The report highlights the following points:
- The current map of control and influence in northern Syria and other provinces that are geographically connected to the north;
- The map of the international and local actors in general, without detailing their influence or the extent of their control;
- Who is controlling the most important resources and infrastructure in the northern region (the most important international roads - International border crossings and their situation).
(Who's/What) controlling the Syrian north region
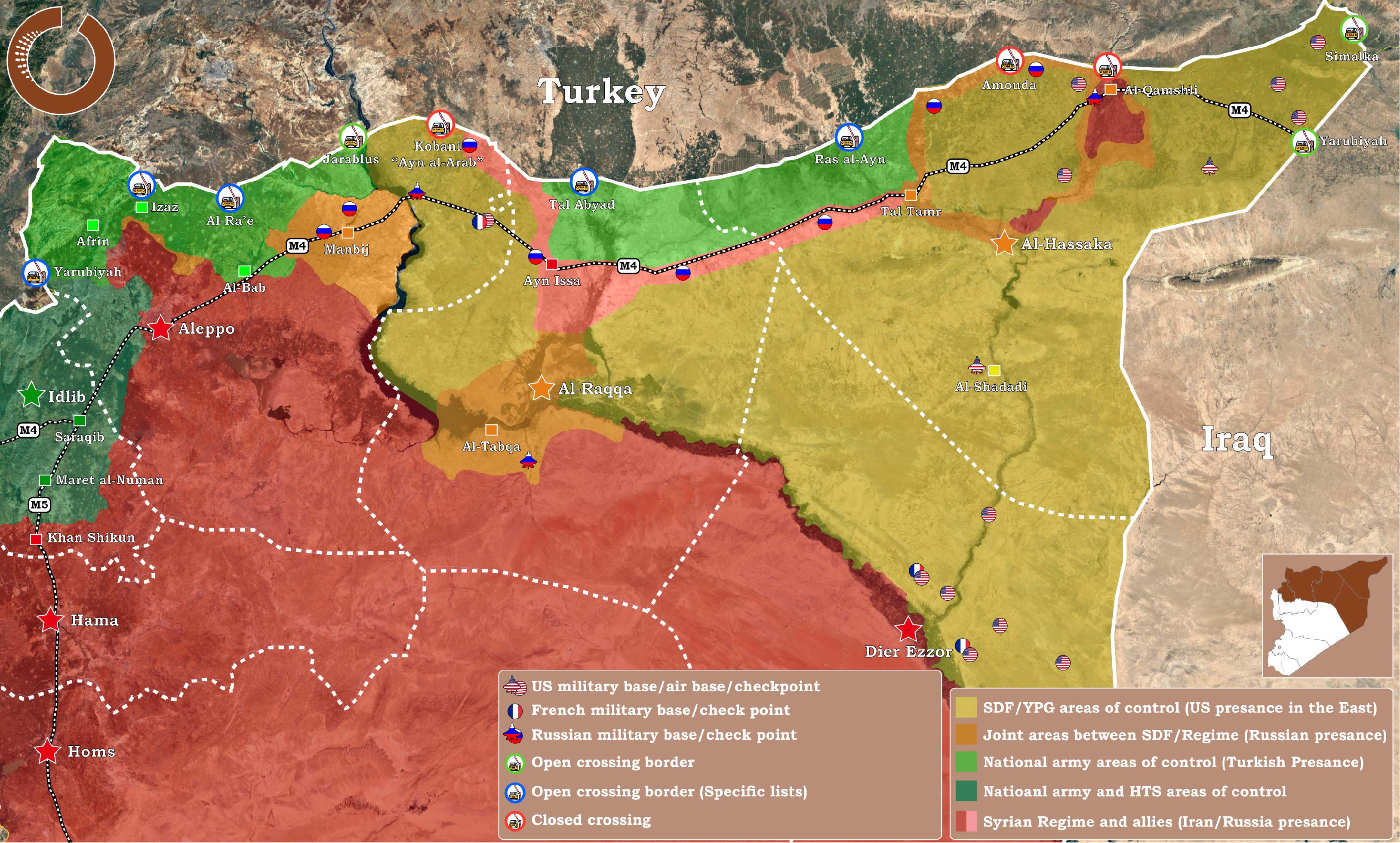 Map 1: Updated areas of control and influence in the Northern region of Syria – 12 December 2019
Map 1: Updated areas of control and influence in the Northern region of Syria – 12 December 2019
| USA | France | Russia | Iran | Turkey | |
| Al-Hassaka | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Al-Raqqa | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Aleppo | - | - | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Idlib | - | - | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Table 1: International direct/indirect presence s in the Northern provinces in Syria – (General look)
| Province Area km2 | Regime Forces | Joint area (Regime & SDF) | SDF | Opposition Forces (SNA) | HTS | |
| Al-Hassaka | 23.334 km² | 4% | 5% | 83% | 8% | - |
| Al-Raqqa | 19.616 km² | 36% | 12% | 42% | 10% | - |
| Aleppo | 18.482 km² | 51% | 11% | 9% | 23% | 6% |
| Idlib | 6.097 km² | 22% | - | - | 33% | 45% |
Table 2: Local forces updated percentage of control in the north provinces in Syria
| M4 Length (Km) | Regime Forces | Joint area (Regime & SDF) | SDF | Opposition Forces (SNA) | HTS | |
| Al-Hassaka | 230 Km | 37% | 5% | 58% | - | - |
| Al-Raqqa | 103 Km | 76% | 24% | - | - | - |
| Aleppo | 195 Km | 22% | 30% | 20% | 17% | 11% |
| Idlib | 73 Km | 14% | - | - | 33% | 57% |
Table 3: Who's controlling M4 road from Iraq (Kurdistan) border to the administrative borders between Idlib and Hama provinces
| Province | Between | Local Forces | International Influence | Crossing situation | |
| Yarubiyah | Al-Hassaka | Syria-Kurdistan (Iraq) | SDF | USA | Open (Aid- US military) |
| Simalka | Al-Hassaka | Syria-Kurdistan (Iraq) | SDF | USA | Open (Aid-Civilians-US military- Journalist) |
| Al-Qamishli | Al-Hassaka | Syria-Turkey | Regime Forces | Russia | Closed |
| Amouda | Al-Hassaka | Syria-Turkey | Joint Presence (Regime/SDF) | Russia | Closed |
| Ras al-Ayn | Al-Hassaka | Syria-Turkey | SNA (Opposition) | Turkey | Open (Aid- TSK) ([1]) |
| Tall Abyad | Al-Raqqa | Syria-Turkey | SNA (Opposition) | Turkey | Open (Aid- TSK-Journalist) |
| Kobani | Aleppo | Syria-Turkey | Joint Presence (Regime/SDF) | Russia/Iran | Closed |
| Jarabulus | Aleppo | Syria-Turkey | SNA (Opposition) | Turkey | Open (Aid-Civilians- Journalist) |
| Al-Ra’e | Aleppo | Syria-Turkey | SNA (Opposition) | Turkey | Open (Aid-TSK) |
| Bab al-Salma | Aleppo | Syria-Turkey | SNA (Opposition) | Turkey | Open (Aid-Syrian Interim Government) |
| Hemame | Aleppo | Syria-Turkey | SNA (Opposition) | Turkey | Open (Aid) |
Table 4: Situation of the international crossing border in the Northern provinces in Syria
Mr. Yaser Tabbara | al-Baghdadi is Dead
On 28 Oct, 2019 M Yaser Tabbara, co-founder of the Omran Center for Strategic Studies, joined The News makers at TRT World to discuss al-Baghdadi’s Death.
An Assessment of Idlib DMZ after 75 Days
Introduction
On 7 Sep 2018, when the Tehran talks ended between Turkey, Russia, and Iran it was obvious that there was no final agreement or disagreement amongst the Astana international players. Everything became more vague except for the postponement of any ground operation by the Regime and it’s allies against Idlib and its surrounding. The Russians decided to postpone any ground attack for the following reasons:
- Buy more time for all the Astana actors to reach for a deal that suits everyone and serves them in a way that does not affect each other's.
- The lack of manpower that is loyal to the Russians in the northwest and that are needed to fill Idlib in case of a ground attack, which will give the chance for the Iranian-backed militias to expand their control to Idlib and Western Aleppo.
Prior to the DMZ agreement, both Turkey and Russia committed to taking several steps in Idlib, which formed the solid base for the initial step of the DMZ. Following are the most significant actions done by Turkey and Russia during the first two weeks of Sep 2018:
- The Turkish observation points cleared their surrounding from any Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) presence.
- Turkey informed al-Jabha al-Watnia factions to stop coordinating with HTS and not to form any kind of joint military operation rooms.
- Russia announced that it took control of the three internal crossing borders between regime and opposition areas "Abu al-Duhur, Mourk, and Qalat al-Madiq," and informed the 4th division and LDF forces to evacuate the area.
The DMZ Specifications
On 17 Sep 2018, Putin and Erdoğan held a meeting regarding Idlib and agreed to establish a DMZ in Idlib, Northern Hama, and Western Aleppo with the following specifications:
- 15 to 20 km zone running along the borders of the Idlib region will be safe from Syrian and Russian air force attack and will be in place by 15 October.
- Heavy weapons including tanks, mortars, and artillery will be withdrawn from the zone by 10 October. ([1])
- This agreement will prevent a large-scale Russian/Syrian ground attack on Idlib and its surrounding.
The agreement was at the time of the announcement the best case scenario for both Turkey and Russia, but mostly it is important for 3.5 million civilians living inside Idlib – on paper the agreement is solid but implementing will not be an easy task.
The DMZ under the Test
The agreement faced many challenges even before it started, several point needed to be addressed by the Russians and the Turks before October 2018. Following are the most threats that directly or indirectly affected the DMZ in OCT and NOV 2018:
-
Al-Jabha al-Watnia are not the only ones who control Idlib and its surrounding, several factions have large presence in the area, and some of them are considered extremists (HTS, Huras al-Dien, Ansar al-Islam – the region also has independent FSA factions, independent jihadist factions, ISIS cells).
-
The Salvation Government which is affiliated with HTS, administratively controls 75 locations (Cities and Villages) in Idlib and it’s surrounding.
-
The Turkish borderline with Syria is totally controlled by HTS including Bab al-Hawa – also HTS controls 2 out of 3 internal border crossings with the Regime areas inside Idlib. Controlling the crossing gate means sizable Income.
-
The Iranian-backed militias have a large presence in Aleppo province and in Northern Hama which the Russians had to insure that their presence would not cause future problem, which as expected didn’t happen, the Russian couldn’t reduce the amount of the Regime and Iranian-backed militias artillery attacks on the DMZ and couldn’t even prevent several ground attacks by them
HTS official statement in regard of the DMZ
On the 14th of October, HTS published a statement clarifying their position regarding the DMZ. ([2]) The statement was vague and didn’t include direct decisions. HTS mainly tried to achieve the following from this statement:
- Win more time to try fixing its own structure and solve the problems between the Syrian and non-Syrian fighters within HTS.
- Give positive signals by seeming to appreciate the efforts and not being a spoiler yet warning against Russian tricks or manipulation.
- HTS warned against any Russian tricks in regard to the DMZ, by that they implied that they accept the deal but do not want to anger the Jihadi side whom HTS gave positive signals to in the first point of the statement about holding on to Jihad
- HTS mentioned the populist protests and said it will give a final decision on the agreement after meeting and consulting with revolutionary sides; this is to show that they supposedly don’t have a problem with the civic movement in Idlib anymore.
HTS extremists, partly led by the Egyptian "Abu al-Yaqzan", refused to accept the DMZ agreement especially because of regime violations and continuous attacks in Hama northern countryside and Western Aleppo countryside where HTS clashed with al-Jabha al-Watnia and captured 25 fighters (majority from Ahrar al-Sham).
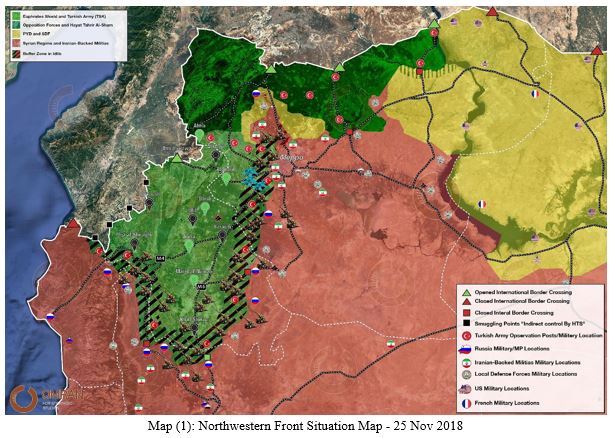
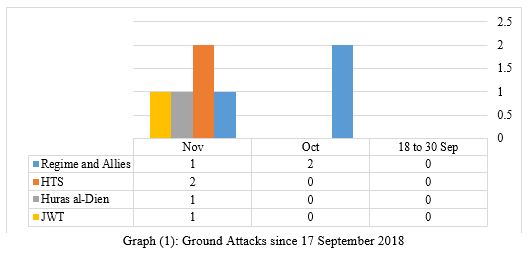
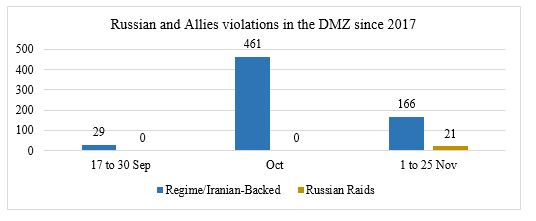
Major incidents in the DMZ and surrounding area from 17 Sep to 10 Nov
- 18 Sep 2018, southern Idlib and northwest Hama witnessed 9+ attacks by regime artillery after the signing of the Russian and Turkish agreement. All the attacks happened in the DMZ and caused the death of 13 civilians.
- 21 Sep, A major explosion occurred in the Hamdaniyah district of Aleppo city. Regime media accused opposition groups of targeting the Military Academy.
- 23 Sep, Hurras Al-Din published an official statement rejecting the Turkish and Russian DMZ agreement.
- 06 Oct, Al Jabha al-Watnia started to withdraw its heavy weaponry from Kafr Naha in western Aleppo.
- 06 Oct, Heavy clashes between HTS and al-Jabha al-Watnia (JWT) in Mirnaz village, causing the death of Seven JWT fighters and five HTS fighters.
- 16 Oct, (Huras al-Din, Ansar al-Din, Ansar al-Tawhid, Jamaat Ansar al-Islam) formed a new operations room to continue fighting against the regime and the Iranian-backed militias, These four factions are listed as extremists.
- 21 Oct, JWT repelled an attack from the LDF and 4th Division fighters near the village Kherbet Al-Naqus in Sahel al-Ghab at Northern Hama.
- 25 Oct, JWT repelled an attack from al-Quds Brigade (LDF) near Kafr Hamrah in western Aleppo.
- 29 Oct, Regime forces bombed Mourk city for the first time since the DMZ agreement. The Turkish Observation Points (OP) is only 0.8 KM far from the city.
- 01 Nov, Jaish Abu Baker (HTS) carried out an attack against a regime location in the eastern Idlib countryside. Pro regime news agency announced the death of six soldiers.
- 02 Nov, The Mourk internal crossing (located on M5), between the opposition & regime controlled areas was reopened. The crossing is controlled by the Salvation Government from the opposition side, and by the 4th Division and Russian Military Police on the regime side.
- 08 Nov, Twenty-three fighters from Jaish al-Izza were killed after the regime and Iranian-backed militias attacked in the village of al-Zilaqiat in northern Hama.
- 09 Nov, JWT launched an attack against the regime position in Mhardeh, killing at least six soldiers from the 5th Corps & 2nd Brigade.
- 10 Nov, HTS "al-Easayib al-Hamrah" launched an attack against regime positions in Halfaya in retaliation for the attack in al-Zilaqiat.
- 10 Nov, Hezbollah participated in al-Zilaqiat attack but until now they didn’t announce any death among their fighters and even if they did they won't declare on which front the fighters were killed.
- 16 Nov, Huras al-Din launched an attack on regime locations near Jurin in Sahel al-Ghab.
- 24 Nov, Regime forces used heavy "240 mm rocket" while targeting Jarjanaz in Idlib, which is part of the DMZ (3 children & 2 women killed).
- 24 Nov, Pro regime news agency reported a gas attack in al-Khaldia district in Aleppo, The substance is currently unknown and it resulted in no deaths so far, with 41 injured according to the regime's state media.
- 25 Nov, Russia warplanes conducted 21 raids on western and southern Aleppo; it was the first Russian attack since 17 Sep the day of the DMZ signing.
Below is a graph of the violations from the regime and Iranian-backed militias as well as the opposition forces and other groups inside Idlib and its surrounding:
Conclusion
The Sochi agreement regarding the situation in Idlib between Turkey and Russia should be considered as an interim agreement imposed by considerations of the situation on the ground and the western / American refusal of any large-scale Russian operation in Idlib. From the Russian point of view, the agreement is a tool for managing the Russian-Turkish relationship on the one hand, as well as to test the western / American position on the other hand. For Turkey, the agreement serves as a tool to contain risks and minimize losses and to a lesser extent a bargaining tool with Russia and America. The Sochi agreement is under extreme pressure, as Iran is actively working to be part of this agreement by exerting pressure on the ground through its militias, like the Zalaqiyat, in north Hama. The internal situation in Idlib has contradictions that seem to be fairly under control so far but this does not eliminate the possibility of exploding at any time via the external stimulation or the result of conflicting calculations (gain and loss) of local forces.
Despite the foregoing, the Sochi agreement is not expected to collapse in the short term, although it may have changed in terms of its parties and field actions, and the foregoing does not eliminate the possibility of limited changes in field control in specific areas, or may alter the field arrangements in those areas; nor will it eliminate the persistence of mutual violations, which reinforce the above-mentioned Russian-Turkish coordination following the recent targeting of Aleppo.
The Turkish-American relationship is not in harmony with regard to the East Euphrates and Manbij, which leads Turkey to resort to the Russians and push Moscow to maintain this agreement.
([1]) 18 September 2018 – The Guardian - https://goo.gl/LC8YeU
([2])Daily News – 15 Oct 2018 - https://goo.gl/yBu41X
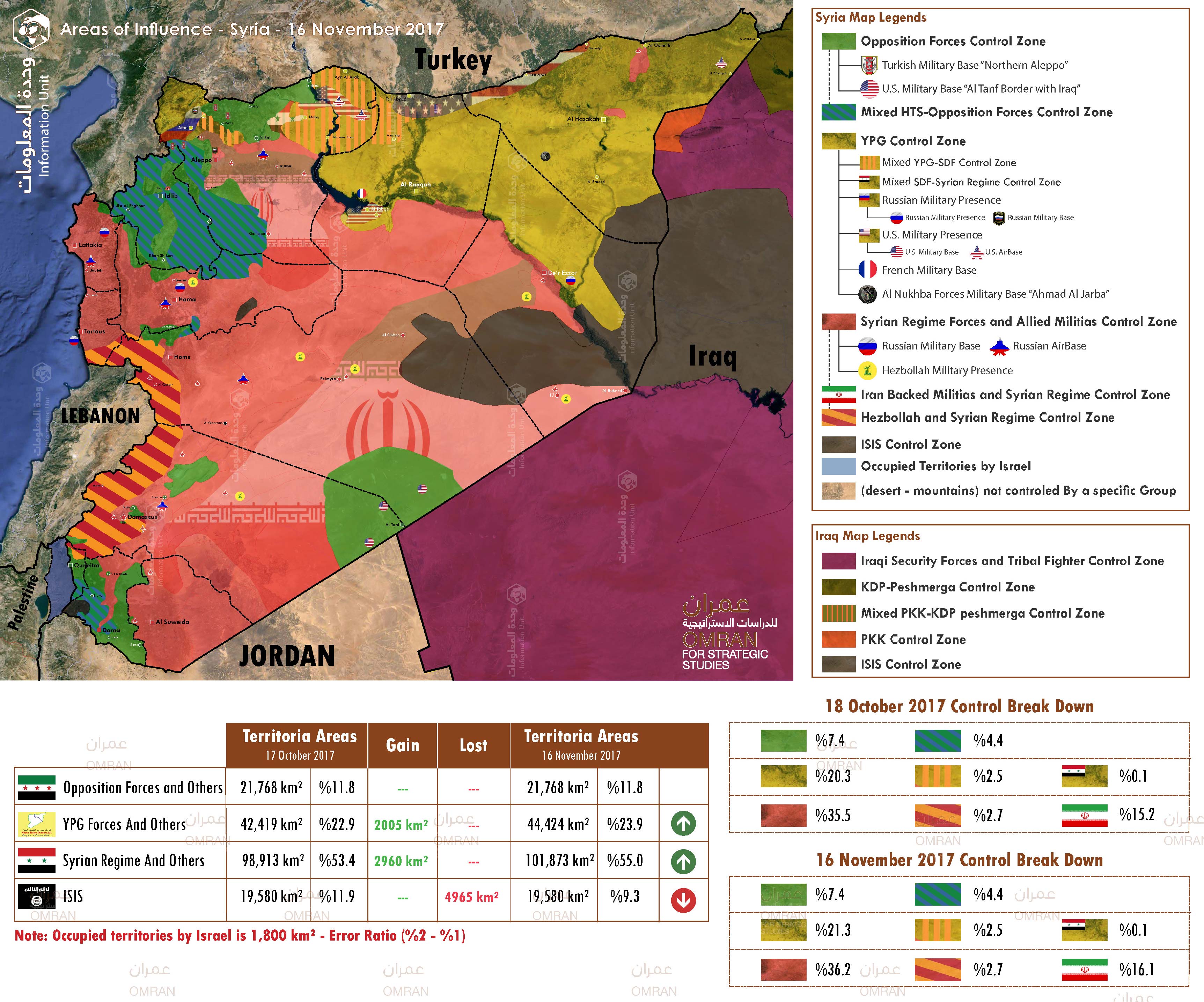
Map of Control and Influence: Syria "16 November 2017"
Damascus
- November 11, unconfirmed reports indicated that Jaish Al-Islam and the Government of Russia reached an agreement stipulating Jaish Al-Islam’s future role as the sole military and political actor in Eastern Ghouta.
- November 12, a UN inter-agency convoy entered Duma city, Duma subdistrict, through Al-Wafideen crossing in coordination with SARC and the ICRC.
- November 15, Ahrar al-Sham launched an attack on the regime forces stationed in the management of vehicles in Harasta, the attack came in response to the regime's repeated attacks on Eastern Ghouta.
Important Note:The humanitarian situation in Eastern Ghouta continues to deteriorate. Bread pack prices reached 1,900 SP, 1kg of rice is currently at 4,000 SP, and most day-to-day essentials are scarce in public markets.
Southern Front
- November 12, Unconfirmed reports suggest the Jordan-based Military Operation Center (MOC) has disbursed its last payment to Southern Front Alliance combatants, as well as its final arms and munitions delivery.
Al Hasakeh
- November 9, SDF established full control over Markada city, in Markada subdistrict, Al Hasakeh governorate.
Important NoteMarkada was considered as the last major city controlled by ISIS in the governorate. Moreover, SDF control over Markada secures its control over the eastern bank of Euphrates River in southern Deir Ez Zor, as well as oil and gas in the area. Nevertheless, reprisal attacks by ISIS combatants remain possible.
- November 12, YPG-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) reportedly handed 52 Russian Chechen individuals, thought to be families of ISIS combatants, to the Government of Russia.
Aleppo
- November 12, Clashes and shelling continued in western rural Aleppo governorate between Noureddine Zinki, a prominent armed group in northern Idlib and northwestern Aleppo, and Hayat Tahrir Al Sham (HTS).
Important Note Clashes reportedly ensued after Hay’at Tahrir Al-Sham attempted to prevent combatants who defected from Hay’at Tahrir Al-Sham from joining Noureddine Zinki in Hayyan and Andan, in Haritan subdistrict, which is controlled by both groups. During the clashes.
- November 13, Syria Regime and aligned forces, allegedly to include Russia, carried out airstrikes on Atareb city, Atareb subdistrict in northwestern Aleppo governorate. Various media sources and local sources have reported casualties at approximately 70 individuals, while several sources reported that at least one airstrike targeted a market in central Atareb city as well as a police station.
Deir Ez Zor/Al Raqqa
- November 8, Syria Regime and Pro-Iran Militias reportedly took control of the Abukamal border crossing, located on the Syria-Iraq border in southeastern Deir Ez Zor governorate.
Important Note as of November 5, Hashd Sha’bi, an Iraqi Hashd Sha’bi militia, took control over Al-Qaim town and its nearby border crossing, opposite Abukamal along the Iraqi-Syria border.
- November 11, SDF reportedly controlled Basira, in Basira subdistrict, and its vicinity, located approximately 32 km south of Deir Ez Zor city.
Important Note 69,047 individuals have been displaced from Abukamal subdistrict to SDF-controlled areas in northern and eastern Syria due to clashes between Syrian Regime forces and ISIS.
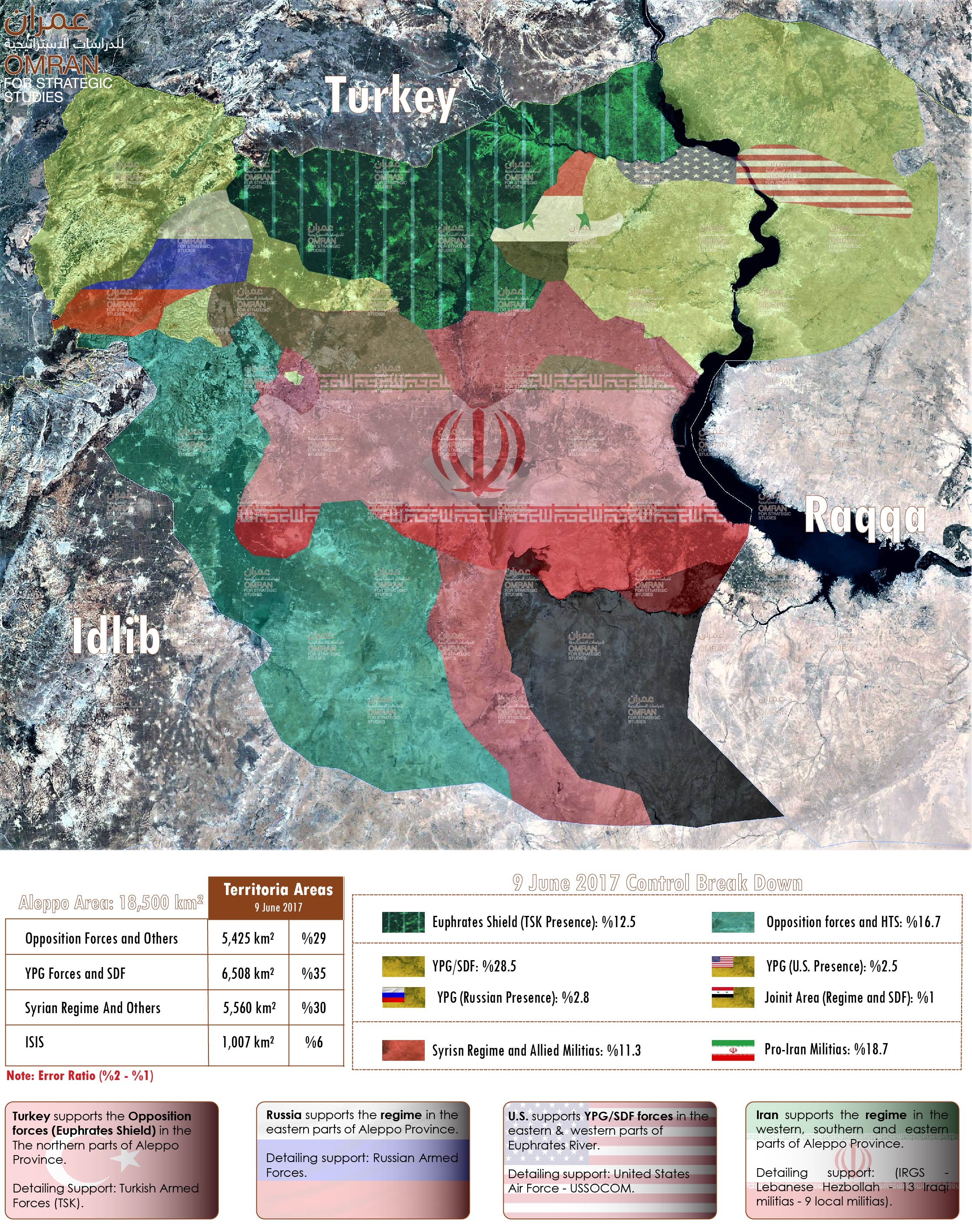
Map of Control and Influence: Aleppo Province "9 June 2017"
Dr. Ammar kahf talking about Turkey's Idlib Operation
Dr. Ammar Al Kahf on 7th of October talking about Turkey's Idlib Operation, he said that there was a delay of the operation in order to contain elements from HTS "Al Qaida" and not to start a fight with them in order to save many life's of civilians, he added that the Astana agreement and three partners "Turkey, Russia and Iran" have different objective and this is not a strategic alliance in any way, but a very tactical step by step approach on containing the HTS forces at the time been, on the issue of Assad there is a political process that’s under going, and he is already lost credibility because of the fact that Russia and Iran are speaking on behalf of the regime and the his not on the table, he ended saying that there are life to save in Idlib and the agreement in Astana says that no Iranian or Russian troops will enter Idlib but they will be in charge of the border control of the de-escalation zone, he also added that one of the major objective in Idlib is to block any SDF advancement from Afrin.