Introduction
Due to the escalating crises and conflicts worldwide, the growing number of individuals requiring relief and humanitarian assistance, and the significant disparity between needs and resources(1),Syrians face complex challenges and responsibilities amidst political deadlocks. This situation necessitates an awareness of the implications for the level of services provided and the number of beneficiaries within Syria, considering the deteriorating social and economic conditions for Syrians in host countries.(2)
According to the Global Humanitarian Overview report issued by OCHA for 2024, approximately 308 million people worldwide require humanitarian assistance, necessitating $48.64 billion to aid 187.8 million people in 70 countries through 36 coordinated response plans. Only 15.3% of the plan has been funded so far, with $7.42 billion in funding, which is 35% less than the $11.40 billion recorded during the same period last year. Additionally, the total reported funding amounted to $4.34 billion, which is 42% less than in 2023 ($7.44 billion). Reported funding from major donors in the first four months of 2024 has also decreased compared to 2023.
Local and Regional Implications
This reduction will have several implications for Syria on the local level, such as worsening living conditions, increased migration waves, heightened militia activity, the growth of the war economy, and involvement in illicit activities such as drug and arms trafficking. Additionally, societal violence, including theft, kidnapping, and extortion, will negatively impact local security and stability indicators.
On the regional level, economic pressures on host countries will increase, leading to a higher likelihood of these countries pushing Syrian refugees to return voluntarily or forcefully and taking measures to tighten restrictions on them. Additionally, the risk of drug trafficking in neighboring countries (Lebanon, Jordan, Turkey, Iraq) may increase, using their territories as transit points to the Gulf and Europe.
Syrian actors in the relief and development field will face several direct challenges, including:
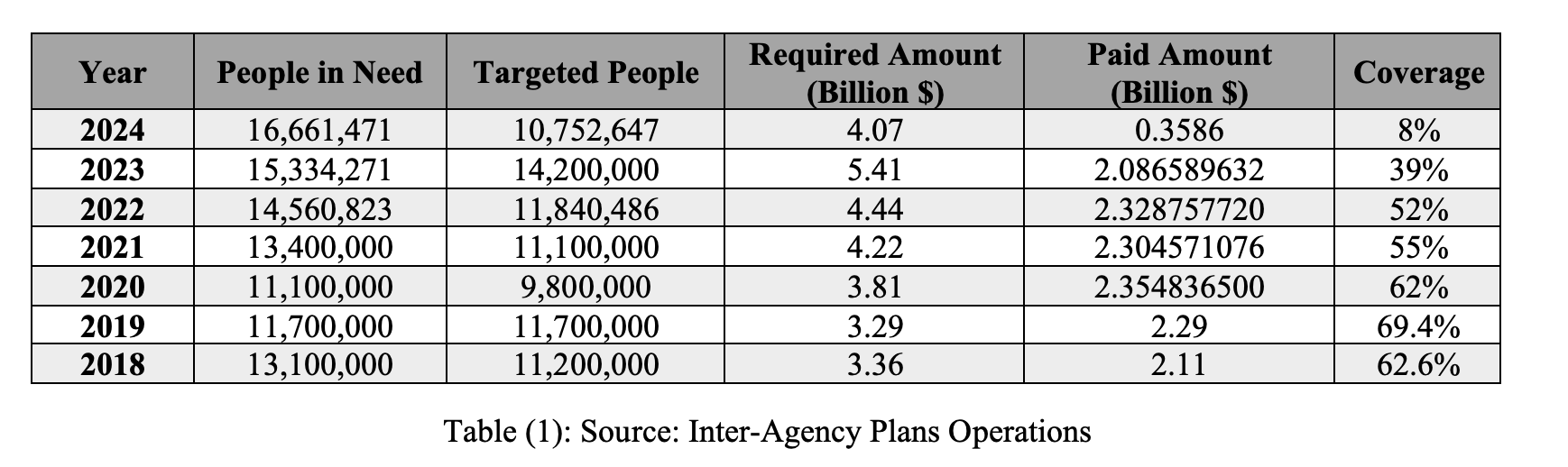
- Severe Food Security Crisis: The reduction in humanitarian funding since 2023 to $2.1 billion (39% of needs) led the World Food Program (WFP) in mid-2023 to reduce the number of people receiving aid from 5.5 million to 3.2 million (a 40% reduction) starting in July 2023. The program announced the cessation of its general food aid across Syria in January 2024 due to severe funding shortages, marking the seventh and largest reduction since the program began its work in Syria.
- Increased Needs: According to United Nations estimates, around 16.7 million people need humanitarian assistance, up from 15.3 million in 2023, the highest number since 2011. Among them, 7.2 million people are internally displaced in scattered areas, including 2.05 million in overcrowded camps.
- Severe Funding Shortages: Only 8% of the required funds have been received, with $358 million collected out of the $4.07 billion needed by May 2024 to meet the immediate humanitarian needs of 10.8 million targeted individuals. Many local organizations in northwestern Syria have had to halt numerous service programs, lay off dozens of employees, and close offices in various towns and cities in the countryside of Aleppo and Idlib.
The following table shows the gradual increase in people in need of humanitarian assistance between 2018 and 2024, in contrast to the decrease in the percentage of funding received compared to the required funding, from 62% in 2018 to 39% last year and 8% this year:
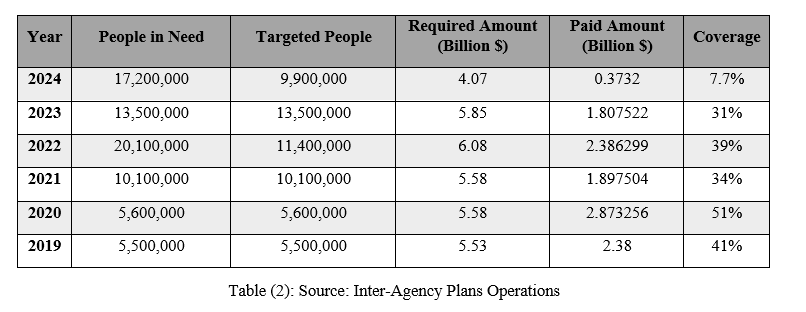
Increased Pressure on Services in Host Countries: It is expected that more than 19 million people will need assistance in 2024, including about 6.4 million refugees and 12.9 million affected members of the host community. Due to reduced funding and the need to prioritize strategically, the collective funding request for 2024 has been reduced to $4.1 billion compared to $5.8 billion in 2023 after reviewing requirements based on priority needs. As a result of the increasing funding crisis, the number of Syrian refugee families in Lebanon receiving cash assistance has been reduced to about one-third in 2024. The World Food Program in Jordan announced a reduction in its monthly food aid to 465,000 refugees in mid-July 2023 and excluded about 50,000 others from monthly assistance due to funding shortages.
The following table shows the increase in people in need of humanitarian assistance in the five host countries (Lebanon, Jordan, Egypt, Iraq, and Turkey) against the decrease in coverage between the required amount and the paid amount.
Deterioration of Services (Water, Sanitation, Care, Electricity, Education): The deteriorating services for displaced individuals in collective centers will increase the risk of resorting to negative coping strategies. About 2.3 million women of reproductive age, including 500,000 pregnant and lactating women, will lose access to essential reproductive and maternal healthcare. Additionally, 2.5 million out-of-school children will miss the opportunity to return to school, threatening the future of an entire generation and depriving children of their basic right to education(3).
Strategic Recommendations
Despite donor pledges during the eighth Brussels Conference for "Supporting the Future of Syria and the Region" amounting to €7.5 billion ($8.1 billion), with $3.8 billion allocated for 2024 and $1.3 billion for 2025, the importance of addressing the potential for funding cuts and reduced aid remains significant. Syrian actors in the political, humanitarian, and developmental sectors must urgently address this challenge through several policies:
- Operational Alliances: These alliances ensure organizational independence while enhancing cooperation and coordination for effective project execution, preventing activity and project duplication.
- Syrian-Designed Comprehensive Response and Recovery Plan: Syrian actors should develop a comprehensive plan as a reference for response and recovery priorities, updated annually.
- Multi-Dimensional Advocacy Policies: Alongside traditional advocacy, innovative advocacy through coalitions can enhance benefits and broaden advocacy efforts both geographically and sectorally.
- Economic Empowerment Policies: Develop statistical and information collection tools, support small and medium-sized projects, and provide vocational training to create job opportunities, thereby reducing dependence on external aid. Implement basic infrastructure projects (water, sanitation, electricity, health, education) to enhance economic recovery and improve living conditions.
Conclusion
International involvement is crucial in Syria's response and recovery efforts. However, the capabilities, networks, and experience of Syrian actors can drive the development of an executive vision for the region's requirements, transitioning them from implementers to planners and implementers simultaneously.
([1]) The disparity between needs and requirements reached an unprecedented level of $31 billion by the end of 2023, with a total paid amount of $24.28 billion, or 43% of the required amount estimated at approximately $56 billion.
([2]) The year 2023 ended laden with significant difficulties and challenges faced by the world, starting with the earthquake that struck Syria and Turkey in February, followed by the conflict in Sudan in April, which left 30 million people in need. Additionally, the Israeli aggression on Gaza resulted in the deadliest humanitarian crisis in the sector since the Rwandan genocide in 1994. Alongside all these crises, conflicts continued in Syria, Ukraine, Afghanistan, Yemen, Congo, Haiti, and other regions.
([3]) Resident Coordinator and Humanitarian Coordinator Mr. Adam Abdelmoula Press Briefing on the humanitarian situation in Syria, 22-03-2024. Link: https://2u.pw/EGrZ56mr




