panel in Brussels Conference entitled: "Harnessing Economic Autonomy for Peace: Reimagining Syria’s Path Forward"
Omran Center for Strategic Studies with Support from SPI organized a side event at the 8th Brussels Conference on Supporting the Syrian people. The panel was entitled: "Harnessing Economic Autonomy for Peace: Reimagining Syria’s Path Forward." Our insightful panelists provided deep dives into economic strategies for peace in Syria.
Dr. Rim Tourkmani outlined Syria's current economic landscape, emphasizing the importance of strengthening local economies to contribute to peace efforts.
Mr. Samir Aita discussed granting regions economic autonomy, focusing on empowering SMEs and strengthening the middle class to impact the peace process positively.
Dr. Sinan Hatahet explored specific economic initiatives that support SMEs and the middle class, highlighting their significance in fostering political negotiations and sustainable peace.
The audience, comprising EU experts and governments' representatives,, development experts, and Syrian civil society leaders, engaged actively and offered diverse perspectives and solutions.
Thank you to everyone who joined and contributed to the enriching dialogue! Your participation is instrumental in driving our efforts forward.
#BrusselsConference
Early Economic Recovery in Opposition Controlled Areas between 2018 -2022
Introduction and Methodology
Early economic recovery aims to support local communities in returning to a stable and normal life, including preventing the community from returning to violence. The Early Recovery Report monitors projects implemented over a period of six months and is issued semi-annually, focusing on the main cities and towns in the "Euphrates Shield","Afrin" and Idlib governorate, which is witnessing remarkable economic activity, within 11 sectors which are: social services, transportation, electricity, water and sanitation, housing and construction, agriculture and livestock, finance, industry, trade, internal displacement, and communications.
The report relied on the official identifiers of local councils and organizations operating on Facebook and Telegram. The data was analyzed according to two levels, the first at the level of economic sectors, and the second by geographical level. Among the monitored areas in the countryside of Aleppo: Marea, A'zaz, al-Bab, Jarabulus, Akhtarin, Qabasin, Bza'a, Afrin, and Al Atarib. In Idlib Governorate: Idlib, Harem, Sarmada, Ma'arrat Misrin, Hazano, Salqin, Armanaz, Termanin, Atme, Al-Dana, Kah, Deir Hassan.
The report aims to analysis and understand the following:
- Monitor the dynamics of the activities and works carried out in the region, thus measuring the development of local economies, and comparing regions and sectors with each other.
- Exploring the ability of local and international actors to create a safe environment for living and working, and the ability of local councils to play a governance role and sign memoranda of understanding with companies and organizations that contribute to providing with the necessary projects.
Distribution of Projects According to Sectors
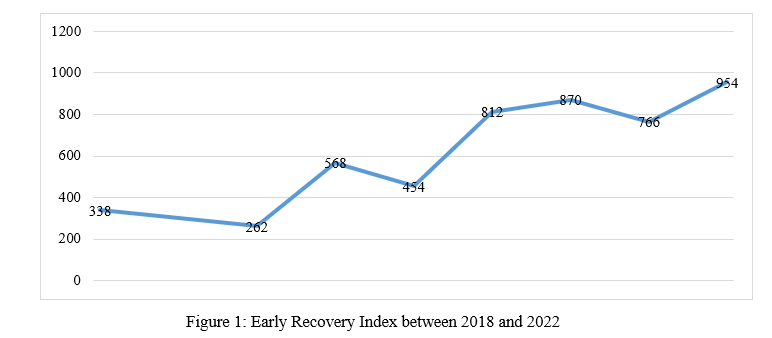
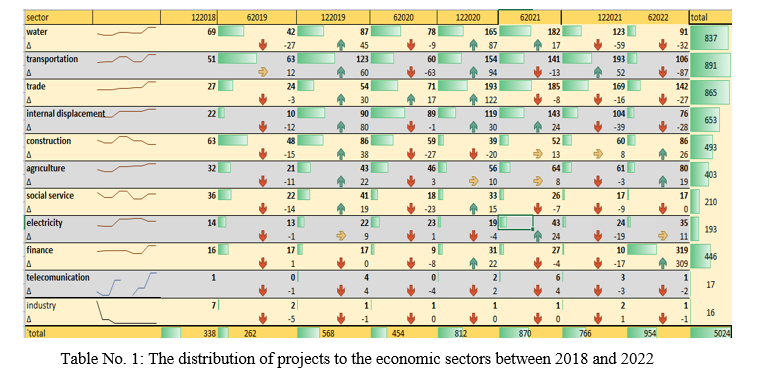
Overall, 5,024 projects were implemented in the countryside of Aleppo and Idlib between 2018 to 2022 through eleven economic sectors. The number of projects rose slowly with 338 projects in the second half of 2018 to 954 projects in the first half 2022 as shown in Figure No. (1) below.
The highest percentage of projects were implemented in the transportation sector compared to the other sectors, as shown in Figure No. (2). These projects mainly contributed to the restoration of main and secondary roads destroyed by the war. These roads were vital to connecting villages and cities and facilitating civilian movement and trade. Water, sanitation, and trade projects came in second and third with 17% each, and the internal displacement sector ranked fourth at 13%.
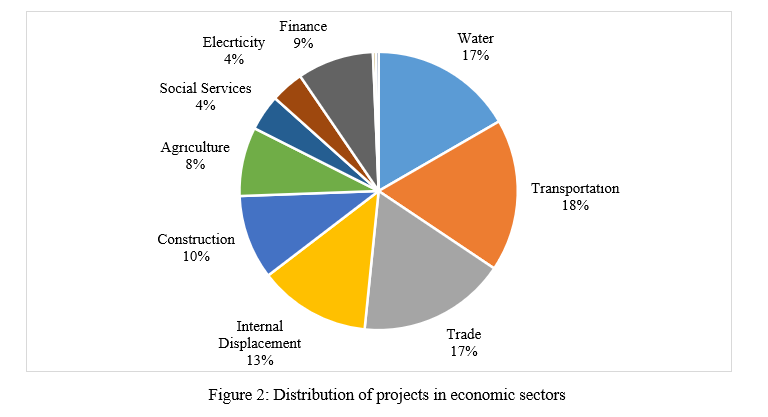
In more detail, Table No. (1) shows the sectoral survey on recovery projects during the observed period, where 891 projects were implemented in the transportation sector, 865 projects in the trade sector, followed by the water and sanitation sector with 837 projects. These projects were central to the recovery process in the region as they extended new water and sewage networks, repaired old networks, performed periodic maintenance, and repaired faults if they occur, such as paving roads, sidewalks, and commercial markets with asphalt and stone. Although these projects are still referred to as relief, they supported 1,293 camps, with a massive number of internally displaced persons, to access support and services. Projects related to construction were relatively low, around 487 projects were implemented, that included residential complexes for those displaced and the issuing of licenses for commercial and residential buildings. Agriculture projects were also lower, as farmers are reluctant to farm, there were only 403 projects during the observed period. The industrial, communications, and finance sectors are also suffering at the bottom of the index, due to the security situation and lack of investment in the region.
Distribution of Projects According to Regions
Figure No. 3 shows the distribution of projects between the countryside of Aleppo and Idlib between 2018 and 2022. The countryside of Aleppo had the largest percentage of projects with 55% about 2,757 projects were implemented in many towns and cities, most notably Azaz, Al-Bab, Afrin, Jarablus, Qabasin, Bza’a, Marea and others. The remaining 2,267 were executed in Idlib, Sarmada, Dana, Atma, Harem and others in Idlib governence.
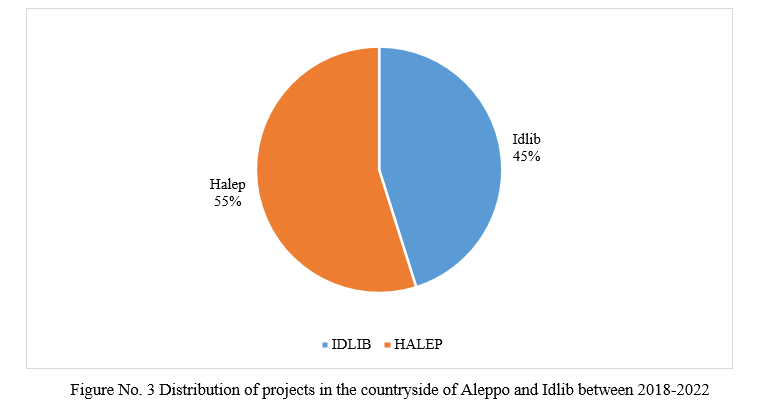
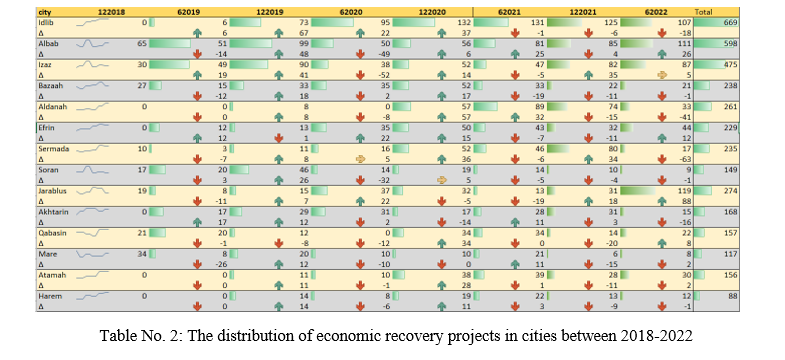
Table No. 2 shows the detailed distribution of projects at the level of towns and cities, where the city of Idlib appears at the top of the index with 669 projects, most of them in the sectors of internal displacement and trade. The city of Al-Bab, in the countryside of Aleppo ranked second with 598 projects in the sectors of housing, construction, trade, water and sanitation, and then Azaz with 475 projects in the sectors of water, transport, and electricity. A number of factors contributed to the discrepancy in the number of projects in cities and towns, including population density, displaced people and organizations, the centrality and importance of some cities before the revolution, the location of towns and cities on trade lines or near crossings, security situation, and lastly the concentration capital in some cities more than others.
Recommendations
Local councils and organizations have implemented important projects that pushed the early economic recovery process forward. Indicators of stability are also more apparent than before. With over four years of monitoring economic recovery activities, reports have highlighted the strengthened national negotiation papers while contracting investment companies to bring in investments. Furthermore, the industry, agriculture, communications, and finance sectors remain a significant challenge in the region’s recovery and attracting funds and investments. This is due to the lack of policies and laws necessary to enhance confidence in the local economy and products, the shortage of raw materials, high prices of raw materials, and the decline in purchasing power, in addition to the fact that the region remains trapped in relief projects.
Among the report's recommendations is to support local councils with good governance policies and implementation within each sector. This would ensure and support workflow, helping them be more attractive for investments. Support in the financial sector would revitalize the other sectors and create a comprehensive identity for the region within the agricultural and industrial sectors. As a result employment oppoturnities would increase, thus supporting residents with more jobs and a sustainabile livelihood.
Significant Economic Cooperation Between The Syrian Regime and Iran During 2018-19
Executive Summary
Iran, a major ally and enabler of the Syrian regime, is increasingly engaged in competition over access to the Syrian economy now that there are new opportunities for lucrative reconstruction contracts. This report sheds light on the economic role played by Iran in Syria through its local representatives and Iranian businessmen. It also explores the (limited) impact of the European Union and U.S. Treasury sanctions on Iran's economic instruments in Syria.
Introduction
Iran has invested heavily in the protection of the Syrian regime and the recovery of its territories. Iran’s main objectives in Syria have been to secure a land bridge between its territory and Lebanon, and to maintain a friendly regime in Damascus. Much of Iran’s investment has been military, as it has financed, trained, and equipped tens of thousands of Shi’a militants in the Syrian conflict. But Iran has also made major financial and economic interventions in Syria: it has extended two credit lines worth a total of USD 4.6 billion, provided most of the country's needs for refined oil products, and sent many tons of commodities and non-lethal equipment, notwithstanding the international sanctions imposed on the regime. In exchange for its commitment to ensuring Assad’s survival, Tehran has expected and demanded large concessions in terms of access to the Syrian economy, especially in the energy, trade, and telecommunications sectors.
Key Iranian Companies
Iran has provided crucial economic assistance to the Assad regime in order to prevent its fall and to ensure that it can meet its fuel needs. In return, Iran demanded access to significant investment opportunities in key sectors of the Syrian economy, notably: state property, transportation, telecommunications, energy, construction, agriculture, and food security.
Since 2013, the Iranians have aided Assad through two main channels. First, it extended two lines of credit for the import of fuel and other commodities, with a cumulative value of over USD 4.6 billion. In order to position itself strategically as the lynchpin of the Syrian economy, Iran restricted the benefactors and implementers of these credit lines to its own national companies. It can thus continue to provide the regime with a lifeline in terms of goods and energy supplies, but in return it can control key parts of the Syrian economy.
The following list includes major Iranian companies that have announced a return to business-as-usual in Syria. Each brief overview gives a description of the company’s involvement in Syria, followed by basic information about the company.
Khatam al-Anbia Construction Base
Has demonstrated an interest in carrying out reconstruction work on Syria infrastructure.
Khatam al-Anbia Construction Base is involved in construction projects for Iran's ballistic missile and nuclear programs. It is listed by the UN as an entity of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), with a role “in Iran's proliferation-sensitive nuclear activities and the development of nuclear weapon delivery systems” (Annex to U.N. Security Council Resolution 1929, June 9, 2010). The company is under the command of Brigadier General Ebadollah Abdollahi.
Khatam al-Anbia conducts civil engineering activities, including road and dam construction and the manufacture of pipelines to transport water, oil, and gas. It is also involved in mining operations, agriculture, and telecommunications. Its main clients include the Ministry of Energy, Ministry of Oil, Ministry of Roads and Transportation, and Ministry of Defense.
Since the company’s founding in 1990 it has designed and implemented approximately 2,500 projects at the provincial and national levels in Iran. It currently works with 5,000 implementing partners from the private sector. An IRGC official recently revealed that a total of 170,000 people currently work on Khatam al-Anbia’s projects and that in the past 2.5 years it has recruited 3,700 graduates from Iran’s leading universities.
Company officials for Khatam al-Anbia include IRGC General Rostam Qasemi and Deputy Commander Parviz Fatah. Other personnel reportedly include Abolqasem Mozafari-Shams and Ershad Niya.
MAPNA Group
- Supplying five generating sets for gas and diesel operations (credit line)
- Construction of a 450 MW power plant in Latakia (credit line)
- Implementation of two steam and gas turbines for the power plant supplying the city of Baniyas (credit line)
- Rehabilitation of the first and fifth units at the Aleppo power plant (credit line).
MAPNA is a group of Iranian companies that build and develop thermal power plants, as well as oil and gas installations. The group is also involved in railway transportation, manufacturing gas and steam turbines, electrical generators, turbine blades, boilers, gas compressors, locomotives, and other related products. The Iran Power Plant Projects Management Company (MAPNA) was founded in 1993 by the Iranian Ministry of Energy. Since 2012, the group has been led by Abbas Aliabadi, former Iranian Deputy Minister of Energy in Electricity and Energy Affairs.
In 2015, MAPNA sealed a USD 2.5 billion contract, Iran’s largest engineering deal to date, to supply Iranian technical and engineering services for the construction of a power station in Basra in southern Iraq.
Mobile Telecommunication Company of Iran (MCI)
A contract to build Syria’s third mobile network (suspended).
MCI is a subsidiary of the Telecommunication Company of Iran (TCI), which is partially owned by the IRGC. MCI brings in approximately 70 percent of TCI’s profits. MCI provides mobile services for over 1,000 cities in Iran and has approximately 66 million Iranian subscribers. It provides roaming services through partner operators in more than 112 countries.
Iranian Companies Active in Syria in 2019
Table 1: List of all Iranian companies with ongoing contracts in Syria - 2019
| Name | Arabic Name | Main Activity | Agreement | Headquarters Address |
| Safir Noor Jannat | سفير نور جنات | Food industries, detergents, and electronics | An old MOU dating back to 2015 to supply Syria with flour | No. 8, Mohamadzadeh st., Fat-h- highway 4Km. Tehran |
| Behin Gostar Parsian | بهين كستر بارسيان | Food industries | No information | Unit 5. No 14. Shahid Gomnam Street. Fatemi Sq. Tehran |
|
Peimann Khotoot Gostar Company جزء من مجموعة PARSIAN GROUP |
بيهين غوستار بارسيان | Electrical power, electronics, and technology | 2017 MOU with the batteries companies in Aleppo, the General Company for Metallurgical Industries in Barada, and Sironix, to carry out electricity projects in several locations in Syria. | Tehran Province, Tehran, District 22, No: 5, Kaj Blvd, 14947 35511, Iran |
| Feridolin Industrial & Manufacturing Company | شركة فريدولين | Electrical appliances | No information | ----- |
| Tadjhizate Madaress Iran. T.M.I. Co. | ---- | Decor and furnishings | No information | No. 198, Dr. Beheshti St., After Sohrevardi Cross Rd., 157783611, Tehran, Iran, Tehran |
| Trans Boost | ترانس بوست | Electricity | Electrical transformer station (230 66 20 kV) in the Salameh, Hama area | ---- |
| B.T.S Company | بي تي سي | Import and export, and commercial brokerage | No information | ------ |
| Nestlé Iran P.J.S. Co. | شركة نستله | Food industries | Supply of milk to Syria for the time being | 6th Floor, No.3, Aftab Intersection, Khoddami St., Vanak Sq., Tehran, Iran |
Recruiting Local Partners (Iran vs. Russia)
Iran and Russia have been competing over the reconstruction of Syria and the potentially lucrative investment opportunities that come with it because both countries hope to recoup some of their outputs from years of supporting the Assad regime and also because both hope to maintain their influence in the post-war era. Both Tehran and Moscow are therefore striving to win over major players in the Syrian political and economic spheres whom they hope to rely on to facilitate their business deals and ensure their respective interests. Consequently, both countries have established economic councils to oversee their ventures and to organize relations with their respective Syrian partners.
The following descriptions of the Syrian-Russian and Syrian-Iranian business councils cover their structures, the total number of members, the most prominent players, and the companies affiliated with their members.
The Syrian-Russian Business Council
The Syrian-Russian Business Council (SRBC) includes 101 Syrian businessmen and a number of Russian counterparts. It is divided into seven committees covering the main sectors of the economy:
- Engineering
- Oil and gas
- Trade
- Communications
- Tourism
- Industry
- Transportation
The Syrian membership of the SRBC includes many influential names, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Members of the Syrian-Russian Business Council
| Notable Names | Total Number of Businessmen |
| Samir Hasan (Chairman, SRBC) | 101 |
| Jamal al-Din Qanabrian (Deputy Chairman, SRBC) | |
| Mohammed Abu al-Huda al-Lahham, (Secretary, SRBC) | |
| Fares al-Shehabi (Businessman) | |
| Mehran Khunda (Businessman) | |
| Bashar Nahad Makhlouf (Businessman) |
Of these figures, three are particularly prominent:
- Jamal al-Din Qanabrian has served as a member of the Consultative Council of Syria’s Council of Ministers since 2017 (the Council presents proposals and consultations to the government on economic and legislative affairs). He is also a member of the Damascus Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
- Samir Hassan, the chairman of the Syrian-Russian Business Council, is a partner in Sham Holding Company, which is owned by Rami Makhlouf.
- Mohammed Abu al-Huda al-Lahham, also a member of the Damascus Chamber of Commerce, is believed to have strong ties with Dhul-Himma Shalish, the powerful Syrian construction mogul and cousin and personal guard of Hafiz al-Assad.
The SRBC also employs a number of Syrian businessmen of Russian nationality, most notably George Hassouani, who was formerly involved in oil and gas deals with ISIS.
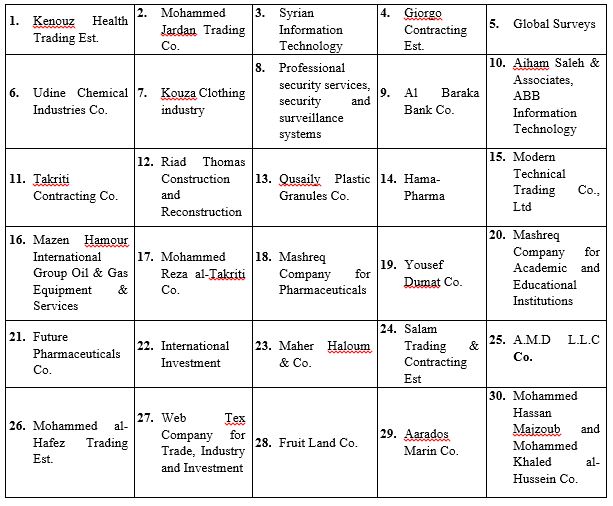
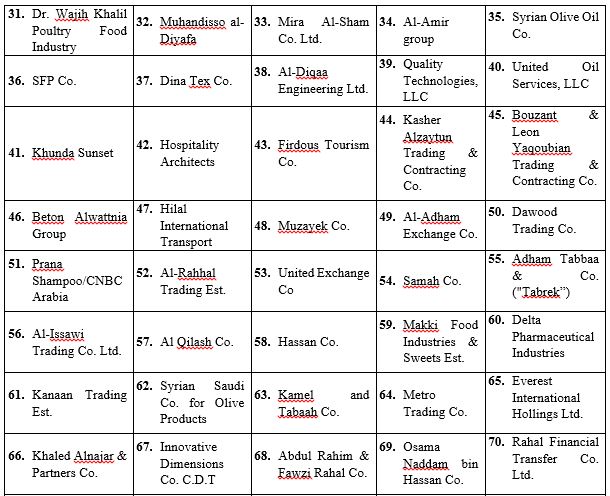
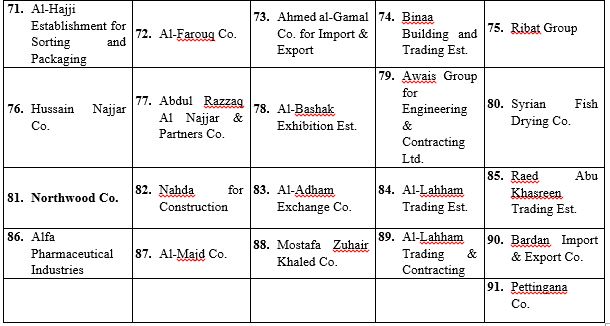
The number of Syrian companies included in the Syrian-Russian Business Council is estimated at 91. These companies are involved in import and export, general trade, textiles, clothing, petrochemicals, energy, and, in a small number of cases, private security operations (see Table 3).
Table 3: Companies in the SRBC
The Syrian-Iranian Business Council
By comparison, Iran has had less success with its business council venture than Russia. The Syrian-Iranian Business Council (SIBC) was established in March 2008, and was initially led by Hassan Jawad. It was reconstituted in 2014 with nine members, as shown below in Table 4.
Table 4: Members of the SIBC
| Notable Names | Total Number of Businessmen |
| Samer al-Asaad (President, SIBC) | b |
| Iyad Mohammed (Treasurer, SIBC) | |
| Mazen Hamour (Businessman) | |
| Osama Mustafa (Businessman) | |
| Hassan Zaidou (Businessman) | |
| Khaled al-Mahameed (Businessman) | |
| Abdul Rahim Rahal (Businessman) | |
| Mazen al-Tarazi (Businessman) | |
| Bashar Kiwan(Businessman) |
Some of these figures have significant economic influence:
- Mazen al-Tarazi is a prominent businessman with investments in the tourism sector as well as in real estate (including the project to redevelop Marota City in western Damascus). He has founded a number of companies in Syria, Kuwait, Jordan and elsewhere that offer services in oil well maintenance, advertising, publishing, paper trading, and general contracting. He also owns a number of newspapers, including Al-Hadaf Weekly Classified in Kuwait, Al-Ghad in Jordan, and Al-Waseet in Jordan.
- Iyad Mohammed is the Head of the Agricultural Section of the Syrian Exporters' Union.
- Osama Mustafa is a member of the People's Assembly, where he represents Rural Damascus Governorate. He served as Chairman of the regime’s Rural Damascus Chamber of Commerce between 2015-2018.
The number of companies owned by Syrian businessmen who are members of the SIBC board is estimated at 10 (see Table 5).
Table 5: Companies Owned by SIBC Members
|
Abdul Rahim & Fawzi Rahal Co. |
Al-Sharq Bank |
| Al-Shameal Oil Services Co. |
National Aviation, LLC |
| Rahal Money Transfer Co. |
Ebdaa Development & Investment Co. |
|
Mazen Hamour International Group |
Development Co. for Oil Services |
|
Dagher & Kiwan General Trading Co. |
Concord al-Sham International Investment Co. |
Because of the relatively small number of Syrian members of the SIBC, Iran is making additional efforts to woe Syrian businessmen. According to private sources, Syrian businessmen are seeking contracts with Iranian companies in return for being granted a share of the value of the contract. Table 6 shows key Syrian figures engaged with Iran.
Table 6: Syrian Businessmen Engaged with Iran
| Name | Position | Name | Position |
|
1.Faisal Talal Saif |
Head of the Suweida Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
2.Mohamed Majd al-Din Dabbagh |
Head of the Aleppo Chamber of Commerce |
|
3.Jihad Ismail |
Head of the Quneitra Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
4.Abdul Nasser Sheikh al-Fotouh |
Head of the Homs Chamber of Commerce |
|
5.Tarif al-Akhras |
Head of the Deir Ezzor Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
6.Osama Mostafa |
Head of the Rural Damascus Chamber of Commerce |
|
7.Adeeb al-Ashqar |
Merchant from the Damascus Chamber of Commerce |
8.Kamal al-Assad |
Head of Latakia Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
|
9.Albert Shawy |
Merchant |
10.Hamza Kassab Bashi |
Head of Hama Chamber of Commerce |
|
11.Amal Rihawi |
Director of International Relations at the Commercial Bank of Syria |
12.Mohammed Khair Shekhmous |
Head of the Hasaka Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
|
13.Elias Thomas |
Merchant |
14.Wahib Kamel Mari |
Head of the Tartous Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
|
15. |
Merchant |
16.Qassem al-Maslama |
Head of the Daraa Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
|
17.Saeb Nahas |
Merchant |
18.Aws Ali |
Merchant |
|
19.Ghassan Qallaa |
Head of the Federation of Chambers of Commerce |
20.Iyad Abboud |
General Manager of MOD |
|
21.Louay Haidari |
Merchant |
22.Ayman Shamma |
Merchant |
|
23.Mohamed Hamsho |
Secretary-General of the Damascus Chamber of Commerce |
24.Bassel al-Hamwi |
Merchant |
|
25.Mohamed Sawah |
Head of the Syrian Exporters Union |
26.Khaled Sukar |
Merchant |
|
27.Mohamed Keshto |
Head of the Union of Agricultural Chambers |
28.Sami Sophie |
Director of the Latakia Chamber of Commerce and Industry |
|
29.Marwa al-Itouni |
Head of Syrian Businesswomen |
30.Salman al-Ahmad |
Union of Syrian Agricultural Chambers |
|
31.Mustafa Alwais |
Rami Makhlouf 's partner |
32.Samir Shami |
Syrian Exporters Union |
|
33.Nahed Mortadi |
Merchant |
34.Gamal Abdel Karim |
Merchant |
|
35.Nidal Hanah |
Merchant |
36.Zuhair Qazwini |
Merchant |
|
37.George Murad |
Merchant |
38.Mohammed Ali Darwish |
Merchant |
|
39.Ghassan al-Shallah |
Merchant |
40.Nasouh Sairawan |
Merchant |
|
41.Mousan Nahas |
Merchant |
42.Anwar al-Shammout |
Owner of Sham Wings Co. |
|
43.Mounir Bitar |
Merchant |
44.Bashar al-Nouri |
Merchant |
|
45.Abdullah Natur |
Merchant |
46.Sawsan al-Halabi |
Director of a construction company |
|
47.Tony Bender |
Merchant |
48.Manaf al-Ayashi |
Foodco for Food Industries |
|
49.Maysan Dahman |
Merchant |
50.Khaled al-Tahawi |
Merchant |
|
51.Samer Alwan |
Blue Planet Energy Co. |
52.Saied Hamidi |
Oil and gas sector |
|
53.Roba Minqar |
Clothing industry |
54.Randa Sheikh |
Clothing industry |
|
55.Harout Dker-Mangi |
Merchant |
56.Alya Minqar |
Merchant |
Iran’s Role in Key Sectors
Iran seeks to obtain lucrative investment opportunities in different sectors of the Syrian economy, whether through tenders or monopolies. The main sectors in which Iran is trying to get full access are: agriculture, tourism, industry, reconstruction, and private security.
Agriculture
- Iran’s ability to match Russia’s investments in the Syrian agricultural sector has been significantly limited by the international sanctions imposed upon it. Since 2013 Iran has extended Syria two credit lines with the total value of USD 4.6 billion, aimed mostly at agriculture. Here is a list of Iranian investments in the sector:
- Supply of wheat since 2015 through the Safir Nour Jannat company"سفیر نور جنت".
- An agreement with the Syrian government to establish a joint company to export surplus Syrian agricultural products.
- An investment of USD 47 million for the second phase of implementation of the Iranian credit line to establish a plant to produce animal food, vaccines, and poultry products.
- A contract to build five mills in Syria at a cost of US 82 million in the provinces of Suweida and Daraa.
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with the Syrian General Organization of Sugar (Sugar Corporation) to establish a sugar mill and a sugar refinery in Salha in Hama in 2018.
- A 2018 MOU between the Federation of Syrian Chambers of Agriculture and the Iranian companies Nero and ITM for the import and distribution of 3,000 tractors.
Tourism
The tourism sector is considered one of the most vital sectors in the Syrian economy: it constituted a 14.4 percent share of Syria’s GDP in 2011 (US 64 billion). It has of course been heavily affected by the war, and tourism revenues decreased from SYP 297 billion (around USD 577 million) in 2010 to SYP 17 billion (around USD 33 million) in 2015, while tourism infrastructure suffered a loss of nearly SYP 14 billion (around USD 27 million) over that same period.
Tehran’s investment in Syria’s the tourism sector has been mostly in religious tourism. For instance, the Syrian Minister of Tourism signed a MOU with the Iranian Hajj Organization in 2015 to bring Iranians and others into Syria for religious tours. There are now estimated to be 225,000 religious tourists from Iran, Iraq, and the Gulf countries visiting Syria each year, and they bring in around SYP two billion (around USD 3.9 million) in revenue.
Industry
The industrial sector contributed 19 percent of Syria’s GDP in 2011, and has suffered losses estimated at USD 100 billion during the war. Iran has several industrial facilities in Syria. These are concentrated in the automobile sector, where they include the Syrian-Iranian International Motor Company and Siamco. Iran has also invested in the glass industry in Adra industrial city. The Iranian Saipa group announced a growth in sales of 11 percent in 2017 in Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Azerbaijan. Car sales in Syria reached a significant level: although it was a third of 2018 sales in Iraq so far, 50,000 cars were sold in Syria last year.
Iran has tried to obtain contracts from the Syrian government in the industrial sector, and a number of MOUs have been signed. They include:
- A 2017 MOU between the Iranian company Bihin Ghostar Persian and General Organization for Engineering Industries to rehabilitate several companies: General Company for Metallic Industries–Barada (located in al-Sabinahis a town in southern Syria, administratively part of the Rural Damascus Governorate), SYRONICS (located in Damascus) and the battery factory in Aleppo.
- A 2017 MOU between the Syrian Cement and Building Materials Company in Hama and the Yasna Trading Company of Iran for the supply of spare parts.
In 2018, the Syrian-Iranian Business Council submitted a proposal for the participation of Iranian companies in the rehabilitation of Syria’s public industrial sector. In addition, the Iranian Ministry of Industry has expressed a wish to establish a cement production company in Aleppo as part of the second phase of implementation of the Iranian credit line.
Reconstruction and Infrastructure
The construction sector contributed 4.2 percent of Syria’s GDP in 2011 and then suffered a losses of USD 27 billion over the next six years. Syrian infrastructure has taken a similarly heavy hit as a result of the conflict, with losses valued at around at USD 33 billion, including over three million destroyed houses or housing units.
Iran’s interests in reconstruction—as with tourism—have a religious tinge and are mainly focused on the areas around sacred Shi’a shrines. For instance, Iran has been asking the Syrian regime for large concessions in Daraya, the old city of Damascus, Sayida Zainab, and Aleppo. Thus far Iran has mostly relied on Syrian intermediaries to purchase real estate, businessmen such as Bashar Kiwan, Mazen al-Tarazi, Mohammad Jamul, Saeb Nahas, Muhammad Abdul Sattar Sayyid, Daas Daas, Firas Jahm, Nawaf al-Bashir, and Mohammad al-Masha'li. Tehran has also relied on Syrian associations such as Jaafari, Jihad al-Binaa, the al-Bayt Authority, and “the Committee for the Reconstruction of the Holy Shrines" to expand and acquire new land in or near the holy sites in Damascus, Deir Ezzor, and Aleppo.
Sanctions against Syria and their Effect on Iran
The ongoing conflict in Syria has prompted international outcry and condemnation, as well as a long list of "red lines" and sanctions. The sanctions currently in place against Syria include an oil embargo, restrictions on certain investments, a freeze of the Syrian central bank's assets within the European Union, and export restrictions on equipment and technology that might be used for repression of Syrian civilians.
The problem with the sanctions on Syria is that they are ill suited to address the situation, in which sanctions are unlikely to work due to the ongoing war. The EU took significant steps very early in the Syrian conflict, essentially deploying its entire sanctions toolbox in less than one year, in contrast to its more common step-by-step sanctions approach. After a few years, the EU realized that this approach was rushed and ineffective and was forced to backtrack on some measures. This learning process showed the EU that an arms embargo is not necessarily the best first way to address a conflict situation.
Appendix
Syrian Companies Affiliated with Iran
| Name | Arabic Name | Main Activity | Agreement |
|
Abdul Rahim & Fawzi Rahal Co. |
شركة عبد الرحيم وفوزي رحال | معمل مواد بناء، تجارة عامة، استيراد وتصدير | حماة/طيبة الإمام، سوريا. |
| Ebdaa Development & Investment Co. | شركة إبداع للتطوير والاستثمار | تجارة عامة، استيراد وتصدير | ريف دمشق |
|
Development Co. for Oil Services |
شركة التنمية لخدمات النفط | الخدمات النفطية | ------ |
| Obeidi for Construction & Trade | شركة عبيدي وشريكه للتجارة والمقاولات | تجارة عامة، استيراد وتصدير، المقاولات | فندق الداما روز بدمشق |
| Talaqqi Company | شركة تلاقي | تجارة عامة، استيراد وتصدير، مستحضرات التجميل | دمشق، كفرسوسة، عقار رقم 2463/ 87 |
| Nagam al-Hayat Company | شركة نغم الحياة | تجارة عامة، استيراد وتصدير، الخدمات الاستشارية | ريف دمشق، يلدا/ دف الشوك/ العقار رقم 507 |
| IBS for Security Services | ---- | --- | --- |
| Al-Hares for Security Services | شركة الحارس للخدمات الأمنية | خدمات الأمن والحماية الشخصية | دمشق |
| Mobivida L.L.C | شركة موبي فيدا | تجارة الأجهزة الإلكترونية، الهواتف المحمولة والإكسسوار، وتطوير خدمات الهواتف والإنترنت | دمشق |
| Al-Mazhor Company for Construction | شركة المظهور التجارية | تجارة عامة، استيراد وتصدير، المقاولات | دير الزور |
| Al Najjar & Zain Travel & Tourism Company | شركة النجار وزين" للسياحة والسفر | السياحة الدينية | نبل، مقابل مستوصف نبل عبارة الضرير / محافظة حلب |
Top Syrian Businessmen Affiliated with Iran
| Under EU Sanctions? | Under U.S. Sanctions? | Visited Abu Dahbi(UAE) in Jan 2019? | Main Position | Closeness of Relationship with Iran | Name in Arabic | Name |
| - | Yes | Yes | Secretary-General of the Federation of Syrian Chambers of Commerce | High | محمد حمشو | Mohammad Hamsho |
| - | - | - | Member of Syrian Parliament | High | حسين رجب | Hussein Ragheb |
| - | - | - | Businessman | High | حسان زيدو | Hassan Zaidou |
| - | Yes | Yes | Member of Syrian Parliament | High | محمد خير | Muhammad Kheir Suriol |
| - | Yes | Yes | Member of Syrian Exporters Union | High | إياد محمد | Iyad Muhammad |
| - | Yes | Yes | Manager of the Federation of Syrian Chambers of Commerce | High | فراس جيكلي | Firas Jijkli |
| - | - | - | Chairman of the Supreme Committee for Investors in the Free Zone | High | فهد درويش | Fahd Darwish |
| - | - | - | Syrian Ambassador to Iran | High | عدنان محمود | Adnan Mahmoud |
| - | - | - | Businessman | Medium | عامر خيتي | Amer Khiti |
| - | - | - | Businessman | High | علاء الدين خير بيك | Alla Ed din Khair Bik |
| - | - | - | Businessman | Low | جورج مراد | George Murad |
| - | Businessman | Low | منير بيطار | Munir Bitar | ||
| Yes | Yes | - | Works in SDF-controlled area and has relationship with Samir al-Foz | High | محمد القاطرجي | Mohamed al-Qtrji |
| - | - | - | Businessman | High | علي كامل | Ali Kamil |
| - | - | Yes | Al-Matin Group General Manager | Medium | لبيب إخوان | Labib Ikhwan |
| - | - | - | Businessman | High | سامر علوان | Samir Alwan |
| - | - | - | Businessman | Medium | ناهد مرتضى | Nahid Murtda |
| - | - | - | Businessman | Medium | مصان النحاس | Musan al-Nahas |
| - | - | Yes | Businessman | High | ربى منقار | Ruba Munqar |
| - | - | - | Businessman | Low | هاروت ديكرمنيجان | Harot Dikrmnjyan |