Syria’s Reserve Military Service Transformations and Objectives
Reserve service has been one of the most significant human resource components of the Syrian Regime Army, yet it has also posed one of the greatest challenges and obstacles for Syrians, especially after 2011. This is due to its extended duration([1]), with recruits unable to ascertain the length of their service or their discharge date.
The Turkish-Russian ceasefire agreement of March 2020 and the cessation of major military operations enabled the army to implement changes in reserve service, along with other reforms within the military and security institutions.
From mid-2023 to mid-2024, the leadership of the Army issued several administrative orders to end the retention of certain categories of reserve service personnel([2]). This occurred before the official announcement of a plan for a "professional army", as stated by the Director of the General Administration of the "Army and Armed Forces"([3]).
This article aims to clarify the current plan for reserve service and the objectives the regime seeks to achieve. Additionally, it will highlight the legal aspects related to reserve service and trace the changes made over the past several years.
Reserve Service Plan:Confirmed to Be 2 Years after All
It has become evident over the years that the regime has implemented new measures related to the army, especially after the appointment of a new Minister of Defense in April 2022([4]). The years of military conflict since 2011 have demonstrated to the regime that an army based on conscripts is neither effective nor reliable. The regime’s lack of trust into its own army stems not only from the military's lack of professionalism but also social and sectarian reasons. Consequently, the regime has found it necessary to shift towards building a “professional army” composed of enlisted (volunteer) personnel, starting with a gradual reduction in the duration of reserve service as the first step toward redefining compulsory military service. However, this transition will take several more years to fully realize, ultimately helping to sustain the solid core upon which the regime has relied in its war against people.
The plan to build a “professional army” began with the army leadership introducing consecutive volunteer contracts for five or ten years. These contracts clearly outlined the substantial benefits provided to new enlistees, including higher salaries and additional bonuses. The new enlistees are exempt from compulsory military service if they complete five years of service and could leave the army upon completing the contract, subject to approval from the General Command. Notably, these benefits were not extended to previous enlistees, including in terms of salaries or entitlements([5]).
Additional administrative orders related to reserve service continued to be issued until the reserve service plan was officially announced in June 2024. The plan is based on three main phases, culminating in a defined reserve service duration of 24 months([6]). The plan is structured as follows:
| Discharge Date | Duration of Reserve Service | Note |
| Phase One | ||
| 01/07/2024 | 6 years | Discharged |
| 31/08/2024 | 5.5 years | Discharged on the specified date |
| 31/10/2024 | 5 years | Discharged on the specified date |
| 31/12/2024 | 4.5 years | Discharged on the specified date |
| Number of discharges by end of Phase One | 46,044 military personnel | |
| Phase Two | ||
| 28/02/2025 | 4 years | Discharged after completing 4 years of service by 31/01/2025 |
| 30/04/2025 | 3.5 years | Discharged after completing 3.5 years of service by 28/02/2025 |
| 30/06/2025 | 3 years | Discharged after completing 3 years of service by 31/03/2025 |
| 31/08/2025 | 2.5 years | Discharged after completing 2.5 years of service by 30/04/2025 |
| 31/10/2025 | 2 years | Discharged after completing 2 years of service by 31/05/2025 |
| Total number of military personnel to be discharged by the end of Phase Two | 105,869 | |
| Total number of military personnel to be discharged during Phases One and Two | 151,913 | |
| Phase Three | ||
| 01/01/2026 | 2 years | Discharged after completing 2 years of service |
Table (1): Reserve Service Plan
According to the official announcement, the plan may undergo modifications in the implementation of certain aspects based on the study of reserve service issues, including age criteria and years of service. The time periods for each of the three phases may be adjusted, either increased or decreased, based on the enlistment rates for compulsory military service and the number of contracted enlisted military personnel.
The large number of military personnel, approximately 152,000,expected to be discharged from reserve service by the end of 2025([7]) indicates significant human resources available to the army. This figure does not include those already enlisted or conscripted for compulsory military service at the time the plan was issued, and contradicts previous estimates and reports that indicated a significant personnel shortage in the army([8]).
The plan also includes a clause for the discharge of enlisted military personnel who complete five years of their new recruitment contract (as fighters) and choose not to continue. These individuals will not be retained or called up for reserve service until five years have passed since their discharge. They are also exempt from compulsory military service. However, they may be called up for reserve service for one year only, which can be served continuously or intermittently. Those with ten-year contracts are fully exempt from reserve service upon completion.
Legal Amendments: Serving the Regime's Interests
After the beginning of the Syrian revolution in March 2011, and due to the circumstances imposed by the conflict, the regime made numerous amendments to the Conscription Law (Legislative Decree No. 30 of 2007) to address gaps revealed by the conflict, despite the law having been recently enacted at the time([9]). Among the revised provisions was Article 26, which pertains to exemptions from reserve service. The first change came with Legislative Decree No. 31 of 2020, which added paragraph (e) to Article 26. This amendment allowed for the exemption of individuals residing outside Syria for at least one year upon payment of a cash allowance of USD 5,000."([10]) This amendment aimed to provide additional foreign currency to the Ministry of Defense's treasury.
At the end of 2022, Law No. 29 of 2022([11]) was issued, amending paragraphs (a) and (c) of Article 26. The amendment made paragraph (a) more specific, categorizing disabilities into three types: partial disability not fit for service, near-total disability, and total disability. Paragraph (c) detailed exemptions for only sons and those considered as such due to siblings affected by seven specified disabilities or ailments([12]). This amendment also coincided with the abolition of Decree No. 174 of 2006, which included the “Physical Fitness System for Conscription”([13]). This system had been used to determine whether a conscript could be fully exempted from service or assigned to field or stationary roles based on permanent health conditions.
The regime did not stop at these amendments. On 1 December 2023, it issued Legislative Decree No. 37 of 2023, adding a new paragraph (f) to Article 26([14]). This provision allowed conscripts for reserve service (enrolled or not) who had reached the age of 40 to pay a cash allowance of USD 4,800 or its equivalent in Syrian pounds, with a reduction of USD 200 or its equivalent for each month of service performed by the conscript. This amendment aimed to generate additional funds for the Ministry of Defense’s treasury. Later, in August 2024, the regime issued Legislative Decree No. 20 of 2024, which lowered the eligible age in paragraph (f) from 40 to 38 years([15]).
Additionally, Legislative Decree No. 20 of 2024 introduced two new paragraphs to Article 26. Paragraph (g) stipulated that conscripts could be exempt from reserve service by paying a cash allowance of USD 3,000 if they could prove they have partial disability not fit for service or near-total disability as listed in paragraph (a). This amendment aimed to offer a lower cash allowance for those with less than total disabilities, in line with the regime’s broader policies on disability, as outlined in Legislative Decree No. 19 of 2024([16]). (h) provided an exemption for military personnel who completed ten years of service under the new enlistment contracts mentioned above.
What Lies Behind the Reserve Service Plan?
The reserve service plan aims to alleviate social pressures in regime-controlled areas, especially following significant waves of men leaving the country to seek asylum. seeking to avoid reserve service is one of the factors, along with security or economic or social reasons. Notably, the regime has suspended reserve service for conscripted officers holding university degrees requiring at least five years of study, as well as those holding higher degrees such as a master’s or PhD([17]), regarding to brain drain as many professionals left Syria in order to avoid military service.
This plan is also closely related to the rate of personnel mobilization within the regime forces([18]).New conscripts are being recruited, and discharged personnel are being replaced by enlistees who were attracted through previously announced enlistment contracts. Thus, the plan remains flexible and may be adjusted at various stages, given that the transformation to a "professional army" is still in its early stages and has not yet fully matured.
Another goal of the plan is to make the benefits of enlistment contracts equal to or even better than those offered by contracts in pro-regime militias, marking a significant shift from previous practices. By offering these contracts, the regime aims to integrate militia members into the official military institution as individuals, rather than as distinct groups. This is especially evident in the raised age limit to 32 years, which suggests an effort to weaken militias by drawing their members into the official forces, without necessarily dismantling the militias entirely at least for now.
In some respects, the regime's plan aims to generate additional funds for the Ministry of Defense's treasury and to leverage reserve service as a tool against society to extort it to generate funds and to keep control over the population. The option to pay a cash allowance in lieu of reserve service was not available until 2020, initially only for those outside the country. By the end of 2023, this option was extended to those within the country who meet the age requirement.
The reserve service issue is one of many critical challenges arising from the conflict since 2011, significantly both the military and social spheres across a large segment of Syrians. The regime approaches this issue with caution and deliberation. While reserve service was an important source of human resources for the regime until 2020, it has since evolved into a revenue-gathering tool, with payments collected from conscripts who wish to avoid service and can afford the cash allowance, both inside and outside the country. The regime’s amendments also portray it as a reformist entity, such as showcasing reform efforts in negotiations with external actors, while this approach focus on its own interests, and without regard for the direct or indirect effects of its policies.
Appendix:
Article 26 of the Conscription Law Issued by Legislative Decree No. 30 of 2007 and All Its Amendments.
Original Article of 26([19]):
The Draftee may be exempted from Reserve Service in one of the following cases:
- Permanent lack of physical fitness for Military Service.
- The remaining children of two parents or one parent, whether both or one are living or dead, both or one of whom have had two children die or become martyred as a result of carrying out a work-related duty in the state or as a result of military operations.
- The only son of two parents or a mother, living or dead, who is effectively the only healthy son to a sibling or siblings who have been afflicted with disabilities or ailments which prevent them from caring for themselves.
- A father who has had one or more son die or become martyred as a result of war operations because of carrying out a work-related duty in the state or as a result of military operations recognized in the regulations.
Amended Article of 26([20]):
The Draftee may be exempted from Reserve Service in one of the following cases:
a. Those permanently unable to perform reserve service, as determined by a medical examination, falling into one of the following categories: (partial disability not fit for service; near-total disability; total disability). (Amended by Law No. 29 of 2022).
b. The remaining children of two parents or one parent, whether both or one are living or dead, both or one of whom have had two children die or become martyred as a result of carrying out a work-related duty in the state or as a result of military operations.
c. The only son of two parents or a father or a mother, living or dead, who is effectively the only healthy brother to a sibling or siblings who have been afflicted by one of the seven specified disabilities or ailments. (Amended by Law No. 29 of 2022).
- First:
- Complete kidney failure.
- Severe intellectual disability resulting in profound cognitive impairment.
- Severe schizophrenia and severe postpartum depression.
- Complete paralysis of one side of the body or all four limbs.
- Total blindness with no vision beyond light perception in either eye.
- Amputation of both lower limbs at the level of the legs or thighs.
- Amputation of both upper limbs at or above the wrist joint level.
- Second: Those in similar conditions may be recommended by the permanent medical committees and approved by the military medical council.
d. A father who has had one or more son die or become martyred as a result of war operations because of carrying out a work-related duty in the state or as a result of military operations recognized in the regulations
e. Those residing outside the territory of the Syrian Arab Republic for at least one year upon payment of a cash allowance of five thousand US dollars. (Added by Legislative Decree No. 31 of 2020).
f. Those who pay the cash allowance (enrolled or not) who have reached the age of 38 must pay 4,800 US dollars or its equivalent in Syrian pounds based on the exchange rate set by the Central Bank of Syria on the payment date. A reduction of 200 US dollars, or its equivalent in Syrian pounds based on the exchange rate set by the Central Bank of Syria on the payment date, is applied for each month of service performed by the enrolled conscript, with partial months rounded up. (Added by Legislative Decree No. 37 of 2023. The age limit was initially 40 but was amended to 38 by Legislative Decree No. 20 of 2024).
g. Those who pay the cash allowance (enrolled or not) of three thousand US dollars, or its equivalent in Syrian pounds as per the exchange rate set by the Central Bank of Syria on the payment date, if the medical examination confirms they fall into one of the categories (lower disability - partial disability capable of performing service). (Added by Legislative Decree No. 20 of 2024).
h. Military personnel who have completed ten years of service under the new enlistment contract (as fighters). (Added by Legislative Decree No. 20 of 2024).
([1]) After completing compulsory military service, men remain eligible for reserve call-up until age 42. Since 2011, conscripts have typically been retained as reservists beyond their initial service. The call-up for reserve service has also expanded to address increased manpower needs and issues of draft evasion and defection.
([2]) “What’s New in the Administrative Order of the Syrian Regime Regarding Military Service” Enab Baladi, Published on: 11/06/2024, Link: https://bit.ly/4d8kr79.
([3]) “Special Interview on Legislative Decree No. 37 of 2023” Syrian News “Al-Ikhbariya| Channel, Published on: 01/12/2023, Link: https://bit.ly/3Sytc2k.
([4]) “General Ali Mahmoud Abbas” Ministry of Defense, Published on: 30/04/2022, Link: https://bit.ly/3WsN4oF.
([5]) “Syrian Defense Militarizes Society with Tempting Enlistment Contracts”, Enab Baladi, Published on: 28/11/2023, Link: https://bit.ly/4ccvnQb
([6]) “Our Goal is to Develop an Advanced Army Based on Enlistees”, Ministry of Information, Published on: 27/06/2024, Link: https://bit.ly/3SzIq6W
([7]) Leaked document of the plan showing the numbers of military personnel in reserve service to be discharged at the end of each phase.
([8]) “The Syrian Regime’s Army is Drained: Figures Confirm the Loss of Human Resources”, Al-Araby Al-Jadeed, Published on: 31/07/2024, Link: https://bit.ly/46Fpzxq
([9]) “Legislative Decree No. 30 of 2007, Containing the Conscription Law” ,The Parliament, Published on: 03/05/2007, Link: https://bit.ly/3EyjJSk
([10]) “Legislative Decree No. 31 of 2020” Syrian e-Government Portal, Published on: 08/11/2020, Link: https://bit.ly/3YBmP1M
([11]) “Law No. 29 of 2022”, Official Gazette, Part One, Issue No. 2, 2023, Page No.: 16, Syria Report, Link: https://bit.ly/3AhLb6E
([12]) Previous reference or see the appendix, updated Article 26, Paragraph /C/.
([13]) “Decree No. 334 of 2022”, Official Gazette, Part One, Issue No. 2, 2023, Page No.: 17, Syria Report, Link: https://bit.ly/3AhLb6E.
([14]) “Legislative Decree No. 37 of 2023”, SANA, Published on: 01/12/2023, Link: https://bit.ly/4dwhyxO.
([15]) “Legislative Decree No. 20 of 2024”, SANA, Published on: 01/08/2024, Link: https://bit.ly/3Yr6Wek.
([16]) “Legislative Decree No. 19 of 2024”, SANA, Published on: 21/07/2024, Link: https://bit.ly/3LULHdi.
([17]) “Special Interview on the Administrative Order Ending Summons and Retention”, Syrian News “Al-Ikhbariya” Channel, Published on: 17/08/2023, Link: https://bit.ly/46yHWUp.
([18]) The regime has set a minimum percentage for human resources in the army that must not fall below a certain level.
([19]) “Legislative Decree No. 30 of 2007, The Conscription Law”, ibid.
Monthly Briefing on the Events of the Syrian Scene - July 2024
General Summary
This report provides an overview of the key political, security, and economic events in Syria during the month of July 2024, examining developments across various levels.
- Politically, the normalization process with the Assad regime advanced with Italy appointing an ambassador to Damascus. Additionally, seven countries submitted a "non-paper" to the European Union, urging it to abandon the Three No’s policy. The regime also expressed its readiness to establish a new relationship with Turkey.
- Security, instability continues to rise across Syria. In the northwest, protests escalated into violence and direct confrontations with Turkish forces, while the region witnessed the largest drone attack by regime forces against civilian targets in rural Aleppo and Idlib in 2024. In eastern Syria, the international coalition is strengthening its positions as Iran-backed militias increase their attacks.
- Economically, exports through the Nasib border crossing continued to decline, and the regime's economic policies have led to increased capital flight and a higher cost of living. The Autonomous Administration in northeastern Syria (AANES) implemented economic policies that negatively impacted the agricultural sector.
Impact of Regional and International Normalization on Local Actors
Amid the ongoing normalization and restoration of relations with Bashar al-Assad, Italy announced the return of its diplomatic mission and the appointment of an ambassador in Damascus. This move coincided with efforts by Italy and six other EU member states to abandon the Three No’s policy that shapes the EU's stance on the Syrian issue. Meanwhile, the Syrian Regime’s Foreign Ministry issued a statement welcoming Turkey's calls to restore relations with Damascus, expressing readiness to establish a new relationship with Turkey based on clear principles, including the withdrawal of illegally stationed forces from Syrian territory and the combating of "terrorist groups" that threaten the security of both countries and linking the normalization of relations between the two countries to a return to the pre-2011 status quo.
The statement shows the regime's willingness to begin the normalization process and respond to Turkey's calls, dropping the precondition of Turkish troop withdrawal before the Erdogan-Assad meeting.
The regional and international normalization process with the Assad regime is progressing steadily, despite the differing motivations of the involved countries. These motivations are primarily security-driven or involve experimenting with alternative solutions under the guise of offering incentives to the regime, based on a step-by-step approach to gradually change its behavior. However, the normalization process is unfolding in a way that favors the regime and serves its interests. Bilateral agreements provide the regime with more maneuvering space, as they are tailored to each country's individual interests. Additionally, these agreements help the regime evade political obligations and the implementation of international resolutions, particularly Resolution 2245.
Domestically, the Assad regime held legislative elections for the fourth term since the adoption of the new constitution in 2012, following years of stagnation in the Syrian scene since the cessation of military operations under the de-escalation agreements. These elections come shortly after the Baath Party elections, which showed Assad's efforts to re-engineer power centers within the party and strengthen his absolute control to make it a disciplined political force aligned with Assad's direction and capable of interaction and leadership in any new political landscape. The regime's insistence on holding the elections aims to project an image of resilience and victory despite the conspiracies and international pressures, while also evading political solutions by claiming to strengthen its popular legitimacy through elections. Western countries considered the environment unsuitable for elections, while official opposition bodies called for genuine democratic elections in accordance with international resolutions, representing all segments of the Syrian people, unlike the current parliament. Additionally, popular and media campaigns opposed these superficial elections.
In northeastern Syria, the atmosphere of rapprochement between Turkey and the Assad regime has raised concerns among the AANES, considering it an existential threat and describing the process as a large conspiracy against the Syrian people. The administration realizes that Turkey's policy shift is strategic, not tactical, and that this rapprochement will reduce its available options and present it with difficult challenges, especially as it – if successful – would close the door to any future agreement between the administration and the regime. This explains the statement by Mazloum Abdi, the General Commander of the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), who affirmed that the Syrian crisis cannot be solved through violence and war, emphasizing the administration's readiness to engage in dialogue with all parties, including Turkey, to end the conflict and reach a political solution in Syria. To ease local tensions, the administration issued a general amnesty law in response to demands from the public, tribal leaders, and dignitaries. The amnesty includes hundreds of prisoners who committed crimes of terrorism and other offenses before the law was issued.
Rising Security Tensions: Popular Protests Increase Instability Indicators
In northwestern Syria, protests involved acts of vandalism against public and private property, including the burning of trucks, the removal of Turkish flags, and direct clashes with Turkish forces at several locations. This followed the acts of vandalism and attacks on Syrian refugees that occurred in Kayseri Province, Turkey, and in opposition to renewed talk of political normalization between Turkey and the Assad regime after Turkish officials' statements on rapprochement, which triggered the protests. Additionally, other factors led residents of these areas to express high levels of anger and frustration due to ongoing neglect of good governance issues, widespread corruption, security instability, and imbalanced civil-security relations, along with the lack of clear boundaries for the nature of relations with Turkey. Meanwhile, the Idlib region saw an escalation in military operations between regime forces and Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), with the regime launching the largest drone attack of 2024 on civilian sites in rural Aleppo and Idlib. HTS continued to carry out infiltration operations against regime forces, the most notable being operations along the Saraqib axis at the beginning of July.
In other areas, the reconciliation model remains characterized by security fragility across different regions. In the town of Kanaker, after the regime imposed a new security reconciliation aimed at enlisting draft dodgers into the army, opponents of the reconciliation attacked a regime headquarters. This reconciliation and the accompanying events come weeks after clashes between regime forces and local militants at the start of the previous month. In Suwayda, the leader of the Mountain Brigade, Marheg al-Jurmani, known for his support of the popular movement in the province and his responsibility for protecting demonstrations there, was assassinated. This assassination is the most significant incident in the province since the start of the popular movement, occurring shortly after the regime brought in security reinforcements to the province. In Daraa, clashes continued between two local groups in the city of Jasim in rural Daraa for over ten days following the assassination of a leader from one of the groups and accusations that the other was behind the attack. In the same province, fighters launched multiple attacks targeting various regime sites in the province, coinciding with roadblocks using burning tires, in response to the kidnapping of a family from the Al-Sanamayn area by a gang affiliated with the 4th Division in rural Homs. The attacks ceased after the family was released.
Meanwhile, 60 people, most of them civilians, were killed in areas controlled by the AANES due to security disturbances, killings, and tribal conflicts, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights. Additionally, ISIS operations continued in areas under the AANES influence, with 21 different security incidents involving shootings, killings with sharp objects, and planting explosive devices and landmines, resulting in six deaths. Meanwhile, the American base in the Koniko gas plant in rural Deir Ezzor was hit by rockets fired by Iranian backed-militias. American planes responded by targeting the surroundings of the seven villages in areas under the control of pro-Iranian militias in rural Deir Ezzor with heavy machine guns. New military reinforcements arrived for coalition forces in the area, including a short-range air defense system called Avenger. The international coalition has also begun constructing observation towers along the Euphrates River in eastern rural Deir Ezzor to monitor the area and control the security situation amid an increase in tribal attacks from the opposite bank on SDF positions and concerns of an Iranian escalation against the U.S. presence in the region.
Syrian Economy in a Vortex of Crises: Declining Exports and Increasing Living Costs
Syrian exports of vegetables and fruits to Jordan through the Nasib border crossing continued to decline significantly during July 2024 due to Jordan's restrictions on truck entry, following repeated incidents where the regime used trucks to smuggle drugs. This forced Jordan to upgrade the border infrastructure, modernize its equipment, and impose strict conditions on trucks coming from Syria. These measures result in significant losses for Syrian farmers and traders due to the spoilage of goods during the long wait at the border. These actions also negatively affect Syrian exports abroad, impacting foreign currency earnings and potentially straining relations with Jordan if drug smuggling into its territory and through it to the Gulf countries continues.
Regarding the ongoing economic stagnation in Syria and the regime's continued inability to develop the investment environment, figures indicate a 44% decrease in the number of registered companies in Syria during the first quarter of this year compared to the same period last year, along with continued capital flight due to worsening economic challenges. The number of registered traders in the Damascus Chamber of Commerce also dropped from 9,890 to 8,200 traders within one year, down from 17,000 traders before mandatory registration in social security. This decline is attributed to the rising costs of business, particularly energy costs and imposed taxes, difficulties in securing essential business supplies due to their high prices, declining competitiveness of Syrian products, and the lack of incentives and facilities offered by the government. These factors have driven many businesses to relocate to other countries.
Regarding the cost of living in regime-controlled areas, the cost of living for a family of five exceeded 13 million SYP in early July, according to the Qasioun Newspaper Index, while the minimum cost of living reached about 8.1 million SYP. Meanwhile, the minimum monthly wage was only about 278,000 SYP, which covers just 2.2% of the average cost of living in the first three months of 2024 and 2.1% in the following three months. This gap between low wages and high living costs exacerbates poverty and increases the number of people in need, further weakening the purchasing power of citizens, deepening the economic recession, and potentially leading to psychological effects on Syrian families, increasing social tensions, and worsening the humanitarian crisis.In the context of shortages of essential services such as gas and electricity, the waiting time for receiving a gas cylinder reached 85 days in Damascus and 100 days in Homs. This has led to a rise in prices on the black market, ranging from 250,000 to 300,000 SYP, adding to the living burden on residents, reducing their ability to meet basic needs, and increasing public dissatisfaction with government policies. Additionally, the growing reliance on the black market to obtain gas and other services contributes to further economic deterioration.
Regarding economic agreements with the regime's allies, the Syrian Battery and Liquid Gas Company in Aleppo signed a partnership memorandum of understanding with the Russian company Bogra Construction, committing the Russian company to supply, install, and equip a complete factory for the company. Despite a previously signed contract between the Syrian company and the Iranian company Tavan worth $41 million, the lack of progress under the contract indicates the fragility of Iranian investments in Syria and the competition from Russian investors in sectors entered by Iran. Reflecting the improvement in relations with Arab countries, the first Syrian Airlines flight arrived in Saudi Arabia after a year of the kingdom's approval to resume flights between the two countries. This move could open more avenues for cooperation between the two countries, positively impacting the regime's financial resources and encouraging other countries to resume air travel with Syria.
In northeastern Syria, the AANES decided to deprive summer vegetable farmers of their diesel fuel allocations, forcing farmers to buy it on the black market at high prices, which increased production costs and led to a 30% rise in local vegetable prices compared to previous years. These decisions are likely to reduce farmers' profit margins and their ability to continue farming. The lack of support could drive them to rely on the black market and pass on the increased costs to the prices of vegetables and fruits, adding to the financial burden on consumers and increasing poverty and deprivation among the population. This decision highlights the confusion in the administration's economic policies regarding planning and support for the agricultural sector, despite their adoption of socialist visions for regional management. In the same context, the quantity of wheat received this season in AANES areas has halved compared to the previous year due to the low purchase price set and farmers' reluctance to deliver their crops. The administration received only 766,000 tons of wheat, while expectations were around 1.5 million tons. The challenges facing farmers in Al-Hasakah have increased due to the lack of support and low local prices compared to the costs borne by farmers, forcing them to buy medicines and fertilizers in dollars on the black market, increasing costs and leading to a loss in the summer season. The decline in wheat received directly affects food security in the region. Farmers' reluctance to deliver their crops results in a growing trust gap between farmers and the "Autonomous Administration," reflecting the inefficiency of the administration's agricultural policies and its inability to meet farmers' needs.
In northern and eastern rural Aleppo, Syrian trucks resumed operations, transporting goods from border crossings with Turkey to northern Syria after a nearly complete halt lasting four years. Turkish trucks had stopped entering northern Syria due to the anger and protests in Syrian cities following the violence against Syrian refugees in Kayseri Province. The resumption of this activity is expected to create job opportunities for more than 700 Syrian truck drivers and around 500 workers in the region, helping to stimulate the local economy, reduce unemployment, and improve living conditions.
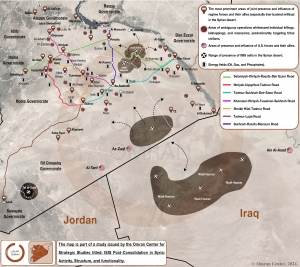
The Syrian Badia: A Map of Influence, Control, and Ambiguous Operations
Following its “defeat” in 2019, the Islamic State (ISIS) adapted in response to both the new scope of its capabilities and the intensified determination of its adversaries. by transitioning from consolidation of power and territorial dominance under a centralized leadership, to a decentralized strategy, relying on autonomous cells and rapid, agile operations. These operations vary in their intensity, patterns, and frequency, depending on the geographic regions and the nature of the forces in control. Operations for which ISIS officially claimed responsibility coincided with other ambiguous operations carried out under its name without an official claim of responsibility. The latter operations targeted both civilian and military individuals and groups through kidnappings and killings.
Although various areas of control have witnessed this type of ambiguous operations, the Syrian desert represented the main stage for it. The period between the 2019 and 2024 saw an increase in operations targeting civilian groups from Arab tribes, especially in the southern desert of Aleppo, which is connected to the desert of Hama, the desert of Homs, as well as the deserts of Al-Rusafa in Al-Raqqa, and Deir Ezzor. Some of these attacks resulted in mass killings that claimed the lives of hundreds of members of tribes in the region, such as Bani Khalid, Al-Amoor, Al-Dulaim, Al-Boshaban, Al-Hadedeen, Al-Gomlan, and Al-Uqaydat tribes. Furthermore, sporadic attacks targeted individuals and groups of shepherds and their livestock, and truffle hunters, rendering the truffle season in the desert deadly.
Several factors contributed to the ambiguity surrounding these operations, notably: the presence of various controlling forces and militias with divergent interests, including ISIS cells that utilized parts of the desert as sanctuaries for launching rapid assaults. The majority of these mass killings transpired on the main highway networks, which is either controlled by Iranian backed militias or is located within areas of their strategic interest, especially in proximity to various energy resources (such as oil, gas, and phosphate) within the region. Moreover, ISIS did not claim responsibility for most of these operations, and their nature differed from what those that ISIS has previously claimed. in terms of tactics and the nature of the targets. Notably, local tribes have accused other forces of being involved in these attacks, particularly the Iranian-backed militias in the region.
The following map highlights the main areas of control in the Syrian desert, as well as key transportation routes, vital energy fields, and areas that have seen ISIS cell activity, and attacks, massacres, and ambiguous operations carried out in ISIS' name between 2019 and 2024.
and to view the map in high resolution: https://bit.ly/44fzTuI
Access the full study (in Arabic) via the Omran Center here: https://bit.ly/3VmhdXC.
Syria's Landscape in 2023: Unrest and the False Sense of Stability
Introduction
Since the onset of the Syrian conflict, marked by a scenario of geographical entrenchment, it has witnessed a plethora of interactions and developments. These range from the structural reorganization of local actors to shifts in the global security and political landscape. The security dynamics in play challenge established boundaries and may lead to either the contraction or expansion of influence zones. Expanding parties will find opportunities to bolster their negotiating positions within the context of political settlements. The political consequences of these dynamics warrant continuous analysis and anticipation, especially considering their implications for international events, including the February earthquake and the Israeli offensive on Gaza.
This report delves into the political, security, and economic trends in Syria, highlighting the strategies of both local and international stakeholders (1).
Between International Isolation and Normalization: A Vague Arab Initiative
Throughout 2022 and 2023, efforts by Iran and Russia to facilitate the Syrian regime's re-engagement with regional countries and its re-entry onto the international stage have intensified. This includes collaboration with Turkey through a tripartite track involving Moscow, Damascus, and Ankara, which Tehran later joined, potentially extending to Arab nations. Despite enhanced security coordination, this path remains fraught with uncertainty due to conflicting interests, such as the regime's reluctance to afford electoral advantages to the Turkish president before elections and disputes over the Turkish military presence in Syria.
The thaw in relations between Arab nations and the Syrian regime has made significant strides, aligning with a regional inclination towards containing conflicts and restoring stability, albeit at the expense of comprehensive solutions. This trend is reinforced by the Arab-Turkish détente, the Saudi-Iranian rapprochement, and steps towards Arab-Israeli normalization.
The February 2023 earthquake in Turkey and Syria catalyzed a political shift that favored the regime by enabling it to solicit international aid and economic support while demanding sanctions relief. The regime's dominance over humanitarian aid delivery points, despite opposition from the United Nations and several countries, highlighted the challenges in aid distribution. This scenario also provided countries seeking normalization with the regime, driven by the “Arab Initiative,” which advocates for dialogue with Assad to achieve a comprehensive solution. This wave of Arab openness began with security and ministerial exchanges leading to the reopening of diplomatic missions in Arab capitals and culminating in Bashar al-Assad's invitation to the Jeddah summit and the restoration of Syria's Arab League membership. The “Arab Ministerial Liaison Committee,” formed under this initiative, focuses on security, counter-terrorism, and humanitarian issues, alongside advancing the political process in accordance with UN Resolution 2254. However, the impact of the Arab initiatives was limited by a lack of strategic vision and effective leverage over the Syrian regime, leading to the suspension of committee meetings due to Arab dissatisfaction with the regime's inaction. This shift towards bilateral engagements has favored the regime, enabling it to sidestep significant commitments while alleviating its isolation.
The year 2023 marked a turning point in the regime's diplomatic engagements, despite opposition from Western nations to normalization efforts. Western responses, including legal actions against Assad for war crimes, highlight the challenges of any normalization attempt, underscoring the complexities of reintegrating Syria into the global community.
A Faltering Political Process and Local Actors Trying to Establish Their Presence
The complexities of the Syrian situation are compounded by the stalled political process, with only the Constitutional Committee remaining active. Despite the stagnation of its proceedings, the committee has been in limbo since its eighth session in mid-2022, obstructing the organization of its ninth session scheduled for July 2023. Efforts by the Arab Liaison Committee to advance the political dialogue have led to the announcement of resumed sessions at the year's end, relocating from Geneva to Amman in response to Russian claims of Geneva's “lack of neutrality.” The regime's stubbornness, its indifference to the Arab initiative, and its refusal to make concessions particularly in light of the Arab rapprochement it perceives as a victory have brought the political process to a crossroads, according to Geir Pedersen.
Two sessions were conducted in the Astana format, with the twentieth potentially being the last in Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan asserts that Astana has fulfilled its aim of gradually ending Syria's regional isolation a view not shared by the trio of involved countries and instead mirrors the regime's preference for a quadripartite path excluding the opposition delegation. The concluding statement emphasized finalizing the normalization roadmap between Turkey and the regime, focusing on the northeast and de-escalation zones, opposing sanctions, broadening humanitarian aid, depoliticizing it, and acknowledging the regime's permission for its entry. This was followed by the twenty-first round on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly, which concluded without a final statement.
The regime faces escalating public unrest due to dissatisfaction with its governance, economic decline in its territories, and rampant chaos and smuggling networks. Assad's indifference was evident in a CNN interview, where he downplayed the Arab initiative's significance, asserting that political relationships are inadequate without substantial support for the Syrian state to control its borders. He insisted that linking early recovery and reconstruction efforts, and thus the returnee issue, to security and political situations is unnecessary, viewing them instead as economic necessities. His continuous emphasis on economic sanctions as a direct crisis cause, coupled with the removal of government subsidies on essential goods, has transformed public frustration into opposition movements in the Sahel, protests in Daraa, and ongoing demonstrations in Suwayda with explicit political demands backed by influential religious and social figures. The regime's attempts to quell public discontent in the Sahel involved replacing the governor, enforcing security control, or manipulating economic networks. In Suwayda, the focus was on preventing the movement's spread beyond the governorate, relying on demonstrators' fatigue and the potential for economic siege if needed. Regarding legislation and laws, the regime abolished the Military Field Court, issued decrees concerning military service, and announced a general amnesty that excludes most political prisoners. These actions are perceived as superficial, intended to appear as “reformist” steps without necessitating real guarantees.
In northwestern Syria, official opposition entities have seen their operational scope diminish due to the political process's deadlock and the regime's recognition as the sole official Syrian representative by several countries. Their activities this year were confined to opening political horizons, diplomatic endeavors following the report condemning the regime's use of chemical weapons in Douma in 2018, support tours for earthquake-affected areas, and limited efforts to curb normalization or advocate for the application of Resolution 2245, restricted to the available margins. Visits aimed at halting military escalation in Idlib were conducted, while the Sweida movement represented a significant opportunity to rejuvenate the issue, albeit not addressed adequately. Internally, opposition groups faced challenges related to their structure, elections, and the circulation of prominent figures among positions, sparking popular discontent. Additionally, the interim government's performance was weak, and the independence of these bodies' decisions was compromised by country-specific determinants.
In northeastern Syria, the Autonomous Administration's efforts were marked by pragmatism. On one hand, it sought to preemptively co-opt opposition forces in anticipation of potential Turkish normalization with the regime at their expense. It collaborated with the Syrian National Alliance Party, which established offices in its territories, and with the National Coordination Body for Democratic Change Forces to form an opposition front endorsing the “National Democratic Change Project.” This initiative, based on five fundamental principles for a successful political resolution involving “national democratic political forces” in accordance with Security Council Resolution 2254, did not alter the administration's stance. Conversely, it expressed willingness to dialogue and cooperate with the regime on its terms, with the potential integration of its forces into the Syrian army under agreeable conditions. However, according to Mazloum Abdi, the regime's rigidity obstructs this possibility. Internally, the Autonomous Administration faced protests concentrated in Deir Ezzor and spreading among Arab tribes in various “civil administrations” regions. Demonstrations were against the SDF's dominion over the area and resources, mismanagement, exclusion of the Arab component, and marginalization of its demands, represented through figures affiliated with the administration. At the Fourth Conference of the SDF, a new council was elected under co-chairmanship, considering tribal balance, represented by “Mahmoud al-Muslat,” with the presence of PYD-endorsed figures and the elimination of the “CEO” role held by Ilham Ahmed since the council's inception in 2015.
The “Democratic Autonomous Administration's social contract in the northern and eastern Syria region” was ratified, designating SDF-controlled areas as a “region” within a confederation, to be followed by general elections in 2024. The contract, more a constitution than a social agreement, was imposed by the ruling party, reflecting its views rather than local perspectives, without consultations representing societal components among local populations. Additionally, the disparity between the articles' text and their implementation, even regarding decentralization a key demand of the Autonomous Administration remains unenforced in its centrally governed areas.
The Gaza War and Its Regional Implications: Open Possibilities
Operation “Al-Aqsa Flood” presented an unexpected turn of events, causing disarray locally, regionally, and internationally. Contrary to the regional trend of containing conflicts and mitigating issues irrespective of solutions, the operation reignited concerns over the potential for war expansion, the reemergence of non-state actors, the advent of new organizations, and the ensuing humanitarian crisis requiring decisive regional responses.
In Syria, the Gaza conflict raised fears of escalation spreading to Syrian or Lebanese territories or drawing any party into participation, particularly with Iran and its affiliated militias and thus the regime considered part of the “resistance axis.” However, Iran's stance remained detached, limiting its involvement to statements, threats, and announcing support for adversarial movements such as the Houthis in Yemen and Hezbollah, which satisfied itself with ineffective missile strikes, alongside a few missiles launched from the Golan for appearances. The regime adhered to Iran's position, responding to Israeli threats with cautious, disciplined statements regarding the Palestinian cause's legitimacy, brutal aggression, and a conspiring world. It notably disregarded “Hamas,” maintaining a steadfast stance despite normalized relations, viewing it as unrepresentative of the broader issue. The regime's participation in the Riyadh summit on Gaza was confined to delivering a speech without objecting to any final statement items, including the two-state solution, civilian casualties on both sides, and establishing normal relations with Israel. Other countries, such as Tunisia, Iraq, and Algeria, expressed reservations, while Iran objected to recognizing the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole Palestinian representative. The regime also prevented public demonstrations condemning the war in its territories, deviating from the norm, settling for specific vigils organized by unions under Baath Party and security service supervision, possibly fearing demonstrations could turn against it.
The official opposition's response was characterized as weak, hesitant, and delayed. The coalition issued general statements of solidarity with victims and condemnation of Israeli attacks, particularly following the targeting of the Baptist Hospital, condemned by the interim government. Meanwhile, the negotiating body largely overlooked the conflict, save for a mention in a final statement from its regular Geneva session and a tweet by the body's head. This cautious approach is attributed to apprehension over potential backlash and the loss of Western support the last remaining political backing for the Syrian cause additionally influenced by Hamas's stance, which had recently reestablished relations with the regime. The position of Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) was more pronounced at the official level, issuing statements supporting the Palestinian cause without mentioning Hamas, alongside official events and fundraising through endowments. Opposition-controlled areas in northern Aleppo and Idlib witnessed significant public demonstrations in support of the Palestinian cause.
The SDF did not articulate an official stance on the conflict, except for a neutral statement by former SDF executive Ilham Ahmed, expressing solidarity with victims on both sides without taking a definitive stand on the aggression. This was despite the historically pro-Palestinian stance of Kurdish organizations, attributed to concerns over the American ally's position, Hamas's proximity to Turkey, and reluctance to express opinions unrelated to the consolidation of the self-administration project.
The Regime’s Systemic and Functional Security Crises
With the escalation of the Gaza conflict into a pivotal international juncture, its repercussions resonated deeply within the Syrian landscape, primarily serving as a conduit for message exchanges and score-settling between Israel and Iran. Meanwhile, the Syrian regime maintained a cautious distance from the conflict amidst Israeli cautions to Iran about the repercussions of its involvement. In this backdrop, international coalition bases faced recurrent assaults, paralleling a series of attacks by Iranian proxies in the region against US and Israeli interests from Lebanon, Yemen, Iraq, and Syria, including selective strikes targeting southern Syria near the Golan Heights. Concurrently, Israel ramped up its attacks on the infrastructure and command echelons of regime forces and Iranian militias, notably executing the assassination of Reza Mousavi, a leading Iranian official in Syria. This move was part of Israel's strategy to weaken the efforts of Iranian militias to fortify their positions following the assault on Gaza, showcasing their military prowess and readiness across multiple fronts.
Domestically, the Syrian regime's security infrastructure grappled with multiple challenges, including bombings and assassinations in supposedly secure regions, such as the Homs and Damascus countryside. A significant incident was a drone attack on a military academy, claiming the lives of 123 regime personnel, including several brigadier generals. This event highlighted substantial security lapses, challenging the regime's security framework and the air supremacy claimed by Russia and the regime west of the Euphrates, as well as contesting the aerial dominance of regional powers amid the advancing military capabilities of non-state actors utilizing drones in Syria and the wider region.
Within territories under regime control, As-Suwayda governorate witnessed an insurrection and popular movement, posing a severe challenge to the regime's narrative of stability and control. The movement in Suwayda, carrying both national and local dimensions, underscored the governorate's strategic significance owing to its proximity to al-Tanf and its role as a conduit for smuggling operations. The regime's strategy to counter this movement involved demonizing it in the media as separatist or foreign-driven, aiming to isolate it on a national level. Moreover, the regime leveraged the strategy of time, withholding services and exacerbating the already dire living conditions to pressure the movement, while attempting to fragment it by exploiting differences among religious and social factions within Suwayda. Despite the movement's impact being confined primarily to Suwayda, its importance lies in challenging the regime's narrative centered on “minority protection,” emphasizing Suwayda's strategic significance in security discussions, particularly regarding smuggling and its proximity to critical security locales.
The ISIS threat persists despite the assassination of its fourth leader by Turkish intelligence, as the organization continues to pose a security risk in Syria and globally. This is manifested by an escalation in the number and quality of operations it conducts, especially in the last quarter of the past year, leading to a marked Russian air escalation, representing a significant counteraction against the organization in 2023. While Jordan has revised its rules of engagement in response to the escalating threat from drug and arms smuggling networks supported by the regime and Iran along its northern border. This adjustment reflects Jordan's growing concerns over the sheer number of these groups, their technological and military capabilities, and the ineffectiveness of Jordanian dialogue with the regime in securing tangible security outcomes. Jordan, since May, has resorted to force, conducting air raids within Syrian territory, and requested Patriot missile systems from the United States to counter the drone threat.
Beyond the Regime's Control: Attempts at Governance and Resistance
In areas under the Autonomous Administration in northeastern Syria, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) encountered several challenges, notably a tribal uprising following the detention of Abu Khawla, the leader of the Deir Ezzor Military Council. This uprising reflects deep-seated structural problems within the SDF's capacity to assimilate the Arab component and redress tribal grievances due to the dominance of the Workers' Party within the SDF's administration. The absence of American initiative to induce changes within the SDF, along with internal tribal challenges and apprehensions regarding potential encroachment by Iranian militias, collectively shape the future prospects of the tribal movement in the region. Turkey has maintained its aggressive posture towards the PKK, designated as a terrorist organization, especially following an incident in Ankara in October. This prompted Turkey to intensify its aerial bombardments targeting SDF military leadership and infrastructure, highlighting Turkey's strategic reach and its reliance on sophisticated drone technology in its counterterrorism strategy.
In northwestern Syria, Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) has launched an unparalleled campaign of internal arrests, detaining members from its administrative, security, and media wings on charges of espionage for the regime, Russia, or the United States. This move signifies HTS leadership's ongoing efforts to consolidate control and neutralize prominent figures, while also capitalizing on factionalism within areas controlled by the National Army to expand its influence.
The Regime's Economic Policies: Burdening Society and State
In January 2023, the Syrian regime initiated a series of bold economic reforms, characterized by a significant reduction in social support mechanisms, placing an increased burden on the market and exacerbating the poverty and living crisis of its citizens. The commencement of 2023 saw the average cost of living in Syria surge to over 4 million SYP for a family of five, with the number of individuals in need of humanitarian assistance soaring to more than 15 million at the start of the year. The devaluation of the Syrian pound continued, with the exchange rate exceeding 7,500 SYP to the dollar by the end of the previous year and recorded at 6,825 SYP by the end of January 2023. The regime's government increased the price of gasoline, marking the second hike within three weeks amid a significant scarcity of petroleum derivatives. Additionally, the Ministry of Economy raised customs duties on all imports by 15-20%, contributing to increased prices for imported goods.
These trends persisted and even escalated in the following months, with the average living costs for a family of five in Syria reaching more than 10.3 million SYP by August, according to the “Qasioun Newspaper” index, up from 4 million SYP in January. Despite salary increases, the average wages, post-increase, did not surpass 200,000 SYP. The regime's economic policies led to a continuous decline in the value of the Syrian pound, surpassing 15,000 SYP against the dollar, with the central bank pricing the exchange rate for remittances at 10,900 pounds. This ongoing devaluation significantly reduced the citizens' purchasing power, rendering salary increases ineffective and exacerbating the population's poverty and living hardships. These developments also underscore the ineffectiveness of the regime's economic management, which addresses the crisis with unproductive solutions.
A significant and economically indicative trend was the increased rate of merchant emigration, especially among traders from Aleppo and Damascus. This included the relocation of significant gold reserves, estimated at around 300 kilograms (approximately 1% of the country's total gold reserves), by top jewelers including (Bashoura, Said Mansour, and al-Jazmati), who moved their entire stock abroad.
Regarding trade relations between the regime and Arab countries, the regime showed considerable interest in economic openness towards Iraq and Saudi Arabia. The Syrian regime appointed an ambassador to the Arab League and conducted visits to Iraq and Saudi Arabia, agreeing to resume economic cooperation with Arab states. Iraq allowed Syrian trucks to enter its territory again at the beginning of the year following agreements between the Syrian Ministry of Transport and the Iraqi side, leading to a 35% increase in trade between Syria and Iraq. Moreover, Jordanian exports through the Nassib crossing in the previous year, 2022, were 23 times the Syrian exports, which only amounted to $20 million.
On the other hand, the regime allowed merchants to import from Saudi Arabia, signing a contract for sugar imports and working on mechanisms to facilitate the movement of Syrian and Saudi trucks in the coming period. The regime stated that there is “no political objection” to importing goods from Saudi Arabia, permitting the import of sugar, chemicals, and petrochemicals. After a hiatus in investments in Syria since 2011, the regime granted licenses in August to two companies owned by Saudi investors to invest in the phosphate, fertilizer, and cement sectors in Syria. The regime's exports of vegetables and fruits amounted to between 500 to 600 tons, with 90% directed to Saudi Arabia, amid almost daily price hikes in the local market due to production shortages and rising costs of raw materials, including fuel, seeds, transportation, and labor. After potato prices surged by 150% in local markets, the Ministry of Economy halted its export when the price per kilogram reached 5,000 SYP, up from 2,000 SYP per kilogram in August, despite the regime's prior approval to export 40,000 tons of potatoes.
In regard to Iran economic activities in 2023, it didn’t spare no effort in 2023 to increase its influence and consolidate its presence in the Syrian economy, with the Iranian Minister of Roads and Urban Development Mehrdad Bazrpash signing agreements with the Syrian regime during an April visit in various sectors including economy, trade, housing, oil, industry, electricity, transport, and insurance. In addition to scheduled plans for stablishing an oil refinery with a capacity of 140,000 barrels per day, adjacent to the existing refineries in Homs and Baniyas, as announced by the Iranian Oil Minister Jalil Salari, to augment the income of Iranian companies. This plan is alongside numerous others set by Iran in Syria over the past years, though sanctions on the Syrian and Iranian oil sectors stand as barriers to maintaining and implementing oil projects in Syria that could fund the regime.
During a visit by the Governor of the Central Bank of Iran, Mohammad Reza Farzin, to Damascus, both sides agreed on a mechanism for using local currencies in trade exchanges between the two countries and establishing communication channels between the central banks to evade sanctions. In the context of bolstering banking and trade relations and joint investments, the Iranian official mentioned Iran's intention to soon open its first bank in Syria.
In December, a Syrian regime delegation in Tehran, led by Prime Minister Hussein Arnous, signed memorandums of understanding in banking, finance, tourism, sports, culture, reconstruction, trade, and the operation of power plants in Syria by Iranian investors. They agreed on zeroing customs duties between the two countries, and the Syrian Central Bank governor discussed with his Iranian counterpart ways to develop trade relations, establish mechanisms for trade exchange in local currencies, and set up a joint bank in Syria. This also includes executing a series of projects by the “Bonyad Mostazafan” foundation, Iran's second-largest investment entity, encompassing 200 factories and financial companies, including a bank and real estate companies, which is internationally sanctioned and directly affiliated with the Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei. This step aims to fulfill Tehran's goal of acquiring a broader share in the Syrian economy.
Aftermath of the February Earthquake: An Alarming Economic Scene
February 2023 witnessed a devastating earthquake that struck northern Syria and southern Turkey on February 6th, affecting over 1.8 million people in northwestern Syria. The catastrophe resulted in the loss of 4,256 civilians' lives, approximately 12,000 injuries, and displaced 300,000 individuals, with children, women, and special needs cases constituting more than 65% of the displaced. The economic losses amounted to $1.95 billion, affecting the public and private sectors and other facilities, while over 13,000 families lost their income sources. The earthquake damaged infrastructure, including 433 schools, 73 medical facilities, and 136 housing units, with over 2,000 buildings collapsing immediately.
The Assad regime saw the earthquake disaster as a lifeline to boost economic activity within its control zones, launching donation campaigns and “for earthquake victims” and receiving financial donations from industrialists in Homs and businessmen estimated at 1.5 billion SYP. Additionally, pro-regime parties and groups exploited the earthquake to campaign for the flow of aid to the Syrian regime and lifting sanctions imposed on it due to crimes committed over the past decade, which restricted its economic activities. The Cross-Border Humanitarian Fund for Syria announced the release of at least $50 million for humanitarian response following the disaster, and the Omran Center for Strategic Studies reported that 23 countries and the United Nations sent approximately 11,772 tons of humanitarian and logistical aid through regime-controlled airports in Damascus, Aleppo, and Latakia. The regime received about 435 trucks of aid from several Arab countries through the Arbaeen, Jadidah, Nassib, and al-Bukamal crossings.
In opposition-held areas in the countryside of Aleppo and Idlib, the region significantly suffered from a lack of aid in the first week of the disaster. The Omran Center for Strategic Studies reported that around 590 trucks, carrying between 5,300 and 7,000 tons of aid, entered from the Bab al-Hawa, al-Salam, and al-Raee crossings between February 9 and 27.
In northeastern Syria, the Autonomous Administration attempted to exploit the earthquake's aftermath to make a breakthrough in its relationship with the opposition by offering a convoy of fuel and medical supplies to the affected areas, which the opposition rejected for reasons including the Administration's insistence on branding the aid with its logos. The Administration announced the opening of all its crossings for humanitarian aid coming from outside its control areas to reach the earthquake victims. In the context of civil and popular initiatives, several civil organizations and social activities in northeastern Syria launched public campaigns to collect financial and in-kind donations from the region's residents and send them to the victims in the affected areas, including the “Tribal Solidarity” campaign, which collected 146 trucks loaded with clothing, household furnishings, food, baby milk, and medical supplies, along with financial donations, and entered the affected areas in northwestern Syria. However, the region later saw a clear decline in humanitarian response operations for the earthquake victims by 35% compared to the end of February, leaving thousands of families unable to secure even one meal a day amidst rising poverty rates and decreasing purchasing power among the population.
Methods of addressing economic impacts varied across influence zones, including periodic salary increases for employees, decisions to regulate markets, and increased control by de facto authorities over economic life. In terms of economic governance, the Autonomous Administration issued two laws to regulate exchange and remittance businesses and the trade and manufacturing of precious metals. The Administration also prohibited the export of dollars from its areas to those controlled by the regime and the opposition, as part of measures to restrict money transfers in and out of its areas, indicating increased financial or cash outflows abroad through smuggling operations, the rise of illegal activities, money laundering, tax evasion, and the Administration's preventive stance towards the available foreign currency reserves.
The Salvation Government in Idlib established a commercial court headquartered in Sarmada city, aimed at addressing disputes and cases arising between traders registered with the chambers of commerce. The court operates in 8 specializations, including intellectual property, bankruptcy, and disputes related to commercial papers, exchange, currencies, commercial remittances, and banking activities. This court's establishment follows a series of decisions, including one to regulate contracting procedures, contributing to the institutionalization and governance of the economy in the region, especially given the multitude of commercial activities and complex trade relations with the existence of the Bab al-Hawa crossing linking Idlib to Turkey. The Salvation Government's efforts aim to attract investors to its controlled areas. While the Interim Government also focused on encouraging investments in its controlled areas, with the Ministry of Finance and Economy announcing the launch of the first Investment Conference in cooperation with Aleppo University in the liberated areas, the Economists Syndicate, and the 2020IDEA foundation. The conference aims to economically develop the liberated areas, improve living standards, increase job opportunities, and resume the entry of UN aid into northwestern Syria through the Bab al-Hawa border crossing with Turkey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Syrian scene remains largely static, with no significant changes expected from international actors or de facto authorities. Despite the regime's political breakthrough following regional normalization and partial restoration of international legitimacy, significant challenges persist, including maintaining influence, navigating ongoing negotiations without concessions, and addressing deteriorating living conditions that could lead to potential unrest. The dynamic security landscape, further complicated by the Gaza war's implications, highlights the intricate interplay between regional actors, local dynamics, and the enduring threats to national security for countries like Turkey and Jordan. This complex scenario emphasizes the evolving nature of the conflict, strategic shifts among local actors, and the continuous need for adaptation to both internal and external pressures.
([1]) For access to the Omran Center's monthly briefings during 2023, see the following link: https://bit.ly/3VXM9hi
Monthly Briefing on the Events of the Syrian Scene March 2024
General Summary
This report provides an overview of the key events in Syria during the month of March 2024, focusing on political, security, and economic developments. It examines the developments at different levels.
- Politically, in its 13th year, the Syrian revolution is mired in political flux. Arab nations strive for reconciliation with Assad's regime, facing opposition from Western and the U.S. insistence on sanctions and normalization rejection. Amid these tensions, Assad's invitation by Bahrain to the Arab summit in May stands out. Concurrently, the push for the Syrian committee's ninth round of meetings by the international envoy is hampered by a location dispute between the regime and opposition.
- Security, the security environment in Syria, shadowed by the Gaza conflict, witnesses an upsurge in violence unprecedented since the halt of broader military operations. In Idlib, Russian airstrikes and regime artillery bombard rural and residential areas, escalating the use of suicide drones against civilians and military targets alike. Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham escalates its assault across Aleppo, Latakia, and Idlib. Meanwhile, the rise in ISIS activities in eastern Syria underscores the SDF's struggles against the group.
- Economically, despite a marginal uptick in the SYP's value, commodity prices soar, unaffected by the currency's stability. A landmark development is Iran's central bank's agreement to establish a joint Syrian-Iranian bank, marking a significant step towards deepening Iranian economic influence in Syria.
Decade Plus Three: Syrian Revolution and the Quest for Resolution
As the Syrian Revolution enters its 13th year, it continues to be marked by some Arab countries' attempts at rapprochement with the Assad regime, contrasted by Western countries' resistance to normalization and the ongoing lack of a viable political resolution. A united stance from the United States, Britain, France, and Germany has been articulated, showing firm opposition to normalizing relations with Assad's regime. They stress the importance of upholding sanctions and the need for a political settlement before beginning reconstruction efforts. Regionally, Bashar al-Assad's invitation to the upcoming Arab summit in Manama, Bahrain, on May 16, along with Faisal Mekdad (the regime's Foreign Minister) meeting his counterparts from Egypt, Lebanon, the United Arab Emirates, and Tunisia, indicates a shift towards nuanced Arab engagement.
Despite Assad's readmission into the Arab League at the 2023 Jeddah summit and the reestablishment of diplomatic relations with several Arab states, notably Saudi Arabia, there seems to be minimal readiness on his part to make meaningful concessions that would promote a political settlement or address security issues stemming from Syrian territory.
On the other hand, the Opposition's Syrian Negotiations Commission (SNC) has accepted an invitation from the UN special envoy to Syria, Geir Pedersen, to reengage in the Constitutional Committee's discussions. Despite agreeing to partake in the committee's 9th round next April, disputes over the meeting's venue persist, highlighting the deep-rooted divisions that complicate progress.
In Northwestern Syria, in Idlib, there has been an upsurge in public protests and civil demonstrations against Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), with demands for improvements in security, administration, and services, as well as the release of detainees. These protests have been partly triggered by a series of arrests for alleged collusion within the ranks of HTS, including the death of a detainee due to torture. In an effort to address the unrest and bolster its internal legitimacy, the group has implemented several measures, including the declaration of a general amnesty and the introduction of structural reforms aimed at pacifying public dissent.
In Northeastern Syria, the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES) has begun preparations for local elections, aiming to strengthen its legitimacy. The ratification of the High Electoral Commission law by the Syrian Democratic Council is a pivotal move toward affirming the administration's role as a legitimate authority over the region's population. However, the integrity of these elections hinges on the establishment of a system for independent and impartial monitoring and judiciary, an infrastructure the administration does not currently possess. Moreover, the decision of numerous political groups to boycott the elections, refusing to acknowledge the ANNES’s authority, suggests that the forthcoming elections may serve more as a symbolic gesture than a meaningful democratic process. This strategy seems to be an effort by the administration to divert attention from security and political dilemmas, alongside public calls for significant organizational reform. The pressing need for reform is underscored by increasing concerns over corruption, nepotism, and ideological control within its bodies, coupled with persistent appeals for the administration to distance itself from the PKK.
Gaza War Echoes: Rising Security Challenges and Internal Conflict
The ongoing conflict in Gaza is influencing Syria's security dynamics, with Israel launching strikes against Iranian forces and their allied militias. These strikes have included targets such as IRGC Military Advisor Riza Zirae in Baniyas, Tartus. The strikes have also hit several sites controlled by Hezbollah, including ammunition depots near Yabroud, Damascus, close to the Lebanese border. Moreover, Israeli operations have been concentrated in the south, particularly in Daraa and al-Quneitra, areas known for the activity of Iranian-backed militias. For a detailed overview of Israeli airstrikes in Syria since the beginning of 2024, please see Map (1).
![]()
Map (1): Map (1): Israeli Airstrikes Targeting Areas with Significant Iranian and Allied Presence & Influence – January 1, 2024, to April 1, 2024
Simultaneously, US airstrikes continue to target Iranian-backed militias in Deir Ezzor and the surrounding regions, resulting in injuries to individuals such as Haj Askar, a commander in the Iranian Revolutionary Guard. These persistent attacks highlight how Syrian territory is being used by regional and international powers to settle disputes and compete for influence. This dynamic is likely to further destabilize the already precarious security situation in Syria amid this power struggle.
Southern Syria is embroiled in a state of security turmoil and targeted violence, with Daraa particularly affected by the assassination of regime officers and security personnel via IED’s and shootings. The region has also experienced civilian deaths due to attacks by unidentified gunmen, underscoring the prevailing lawlessness. Efforts by local forces to target groups suspected of ISIS affiliations and individuals engaged in drug trafficking have been reported, including the notable killing of Shaker al-Shuwaier in Salkhad. The resurgence of drone technology for assassination purposes adds a layer of complexity to the already challenging security situation in southern Syria. These incidents of violence are part of a larger narrative involving ongoing reconciliations and the interaction between various local entities, such as regime forces, factions involved in settlements, and criminal organizations.
In Northwest Syria, Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) has intensified its military actions against regime forces, resulting in both casualties and equipment losses. This increase in hostilities occurs alongside escalated Russian and regime airstrikes in the region, leading to a spike in violence. This includes the deployment of suicide drones by the regime, targeting both military and civilian objectives.
Eastern Syria has witnessed a surge in attacks by ISIS cells, challenging the Syrian Democratic Forces' (SDF) strategy to counteract them. In response, the SDF has executed targeted security operations to mitigate this threat. Notably, a recent operation by the Asayish forces against ISIS cells in al-Hasakah led to multiple arrests. Moreover, disturbances within SDF-administered prisons in al-Raqqa, including riots that resulted in casualties, signal underlying issues of discontent, and demands for improved treatment of detainees, particularly those linked to ISIS.
Inflation Outpaces Syrian Pound's Exchange Rate Improvement
In the Regime held-areas, the Syrian Pound (SYP) saw a modest increase in value against foreign currencies in March, driven by a combination of factors:
- A significant 50% rise in foreign remittances during Ramadan alleviated some of the pressure on the currency.
- A reduction in foreign trade activity led to a decreased demand for dollars.
- The demand for the SYP increased as individuals sold foreign currency to manage Ramadan expenses.
- The regime's government lowered the exchange rate for remittances by 100 liras, aiming to bridge the gap between the official and black-market rates and promote the use of formal channels for foreign currency inflows.
These factors collectively led to a temporary strengthening of the Syrian Pound. However, it's important to understand that this improvement is temporary and not due to monetary policy adjustments by the regime's Central Bank or improvements in production and foreign exchange reserves. The value of the lira is anticipated to fall after Ramadan.
Despite the lira's improved exchange rate, the cost of essential goods and materials continued to rise, with price increases exceeding 100% compared to the previous Ramadan. This indicates that the purchasing power of the population remains significantly compromised, largely due to the regime's policies, such as repeated increases in energy prices, prompting traders to guard against these hikes. Additionally, the regime continued to export vital crops and agricultural products, including staples like potatoes, garlic, and onions, despite domestic demand. The regime has decided to permit the export of various agricultural products, regardless of destination.
Iran is further expanding its influence within the Syrian economy, with the Central Bank of Iran authorizing the establishment of a joint Syrian-Iranian bank. This new bank is expected to facilitate financial transactions and enhance trade between the two countries. This move is in line with amendments to the Syria-Iran free trade agreement, which reduced customs duties on traded goods from 4% to 0%, likely increasing the presence of Iranian products in the Syrian market.
In the Opposition held-areas, the Salvation Government (SSG) in Idlib has eliminated certain fees for residential construction to ease recent protests against HTS. The SSG's Health Ministry also introduced regulations for the health sector, requiring licenses for pharmacies and medical supply stores.
In the countryside of Aleppo, basic commodity sales have plummeted by 50% due to skyrocketing prices and reduced purchasing power, in stark contrast to the previous Ramadan. Notably, meat and vegetable prices have surged, with meat prices increasing as regional traders buy up large quantities of sheep for smuggling. Additionally, investors have begun a project to build an earthquake-resistant residential city near al-Ra'i, which will include /1,500/ apartments.
In the SDF held-areas, the AANES has halted the export of sheep and cattle in response to a rise in local meat prices. Furthermore, fuel prices have skyrocketed by 170% without any formal announcement from AANES officials. Bread prices have also doubled, and vehicle registration fees have been adjusted to reflect the vehicle's year of manufacture, placing additional financial strains on residents, and diminishing their quality of life.
Side Event at the 8th Brussels Conference on “Supporting the Future of Syria and the Region” | Harnessing Economic Autonomy for Peace: Reimagining Syria’s Path Forward
Concept Note for Side Event at the 8th Brussels Conference on
“Supporting the Future of Syria and the Region”
Harnessing Economic Autonomy for Peace: Reimagining Syria’s Path Forward
Date: 29 April, 2024
Time: 16.00 CET
Venue: Thon Hotel EU Brussels
Rue de la Loi 75, 1040 Bruxelles, Belgium
https://maps.app.goo.gl/hz9wWcmWy7MvWQN6A
Registration link: https://ee.kobotoolbox.org/x/of8LLPG2
1. Event Context
In the backdrop of the 8th Brussels Conference on Supporting the Future of Syria and the Region, this side event will explore the role of economic factors, including economic autonomy, in facilitating peace in Syria. The 90-minute panel will focus on economic empowerment at various levels, particularly emphasizing the support and empowerment of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and the middle class as pivotal elements in the peace process.
2. Objective
To discuss and analyse the extent to which economic factors, particularly the empowerment of local economies, can be instrumental in fostering peace in Syria.
3. Panelists
- Dr. Rim Tourkmani.
- Mr. Samir Aita.
- Dr. Sinan Hatahet.
4. Format
- Duration: 90 minutes
- Structure: One panel discussion divided into three thematic sections, followed by a Q&A session
5. Panel Structure
- Economic Foundations for Peace in Syria: will provide an overview of Syria's current economic landscape and discuss how strengthening local economies can contribute to peace.
- The Role of Economic Autonomy and Decentralization: will discuss granting regions economic autonomy, focusing on how this can empower SMEs and strengthen the middle class, thereby positively impacting the peace process.
- Practical Economic Initiatives and Peacebuilding: will explore specific economic initiatives that support SMEs and the middle class, underlining their significance in fostering political negotiations and sustainable peace.
6. Expected Outcomes
- A nuanced understanding of the relationship between economic empowerment and peace.
- Insights into how economic autonomy can be leveraged to support these critical economic segments.
- Recommendations for policy and practical measures to promote economic-driven peace efforts.
- Recommendations for policy and practical measures to enhance the role of SMEs and the middle class in Syria’s peacebuilding efforts.
7. Target Audience
EU and international policymakers, development experts, Syrian civil society leaders, academics, and media representatives.
8. Concluding Session
- Summary of discussions, key insights, and policy recommendations.
- Strategies for implementing economic autonomy and local empowerment in Syria, as well as initiatives that support SMEs and empower the middle class in Syria.
- Proposal for a follow-up mechanism to track the impact of economic initiatives on the peace process.
From Settlement to Captagon: The Security Dynamics in Syria’s Daraa
The Captagon problem has been one of the most critical security dilemmas for Jordan, due to the increasing attempts of drug and weapon trafficking into its borders that became a threat to Jordan’s national security according to a formal assessment paper, along with the ineffectiveness of the current mechanisms to deter the actors involved in Captagon, particularly Iran-backed militias and the Syrian regime. Although the 2017 de-escalation agreement is supposed to grant Iran-backed militias being pushed back 40 km from the Jordanian border, Russia has not completely fulfilled its pledges. The Russian-sponsored settlements of 2018 and 2021 have failed to introduce a security-providing environment through the DDR process of opposition armed groups in Syria’s Daraa.
The security dynamics of the settlements have played a crucial role in creating a Captagon-friendly environment i.e. the absence of a hegemon actor with the involvement of Russia, Iran, and the regime, in addition to former opposition groups which underwent a transformation process in terms of their motivations (political or economic) and objectives of the use of force (zero-sum or variable-sum). Many of the armed groups that had fought fiercely against the Syrian regime gave up on their political aspiration and became involved in Captagon trafficking. This article provides insight into the security landscape, particularly the interconnection between security and Captagon, as a war economy dynamic, in Syria’s Daraa, and ultimately proposes alternative policy scenarios.
The Status Quo of the Settlements
The settlements of 2018 and 2021 between the Syrian regime and opposition factions under Russian auspices resulted, mainly, in the piecemeal return of the regime’s security apparatuses to the governorate, and the integration of many opposition fighters into these apparatuses, without achieving concrete progress vis-a-vis the detainees or forcibly-disappeared persons in regime’s prisons. Since the first settlement, Daraa has been characterized by a fragile security with the prevailing wide scale, politically motivated to a large extent, violence against various civil and armed individuals, let them be affiliated with the opposition or the regime.
Assassinations and detentions, at which dozens of individuals are targeted monthly, have been the regime’s tools to eliminate his opponents relying, for the most part, on the Military Intelligence Branch of Daraa/Swayda, led by “Loay al-Ali”– an EU, UK, and Canada sanctioned Brigadier-General who was promoted to his current position before the 2018 settlement after he served head of the military intelligence/Daraa section between 2011 and 2018.
Thus, the regime rested on a variable-sum use of force to strengthen its territorial control, eliminate opponents, benefit economically from Captagon trafficking, and underpin its central role in the settlement status quo. Yet, even the transformation of regime behavior from zero-sum to variable-sum is mainly a result of Russian diplomatic coercion and the externally imposed status quo in Syria i.e. the relatively frozen conflict that started to arise in 2018.
The Transformation of the Opposition Armed Groups
Former opposition armed groups in Daraa have pursued different survival strategies to cope with or counter-balance the increasing security leverage of the regime in the governorate. Their transformations have generated different types of armed groups with varying motivations and objectives. While the 8th brigade became mainly motivated by preserving the settlement’s status quo that granted the brigade territorial control over some localities and a maneuvering ability to expand influence; other groups, many of which became associated with the regime, have relinquished their political motivations for economic ones through getting involved in Captagon trafficking and/or thuggery activities.
The 8th brigade led by the former opposition commander, Ahmed al-Oda, and composed mainly of former opposition fighters of “Sunna Youth Forces,” has maintained its territorial control in Eastern Daraa’s Busra al-Sham since its establishment under Russian auspices in the aftermath of the first settlement in 2018. Given the relatively secure environment with the lowest assassination rate and the better governance services in areas under its control in comparison with other areas in Daraa, the brigade has managed to preserve social support and counterbalance the regime’s influence seeking to preserve the settlement status quo. Yet, the brigade increased its leverage through variable-sum use of force.
The 8th brigade conducted multiple security operations against ISIS or groups accused of ISIS affiliation in different parts of Daraa such as Jasim in Western Daraa in August 2022 and Daraa al-Balad neighborhood where the operation eliminated the Hafo-Harfoush militia in December 2022. These operations were conducted after the regime’s escalation and threats to launch offensives in these areas under the pretext of ISIS cells, in which the 8th brigade capitalized on the social rejection of the regime’s interference and its connections with local Sheikhs and dignitaries. In addition to its previous intermediary role between the regime and local communities to ease escalation such as the cases of the 2022 March escalation in Jasim and the 2020 February escalation in al-Sanamayn city Northwestern Daraa. Moreover, the 8th brigade has also targeted other groups involved in Captagon trafficking in Northeastern Daraa including a group affiliated with Fayez al-Radi, a former opposition commander assassinated after an escalation with the 8th brigade.
Other groups such as those led by Mustafa al-Masalmeh and Imad Abu Zureiq, the two former opposition commanders, have not only given up their political struggle against the regime after the settlement but also became affiliated with the regime, as they became motivated by economic motives under the new status quo, where the regime became superior. As such, they have been involved in trafficking Captagon drugs, imposing levies on locals, and conducting assassinations against regime opponents on behalf of the military intelligence – which is managing militias and receiving levies from them.
By April 2023, both Abu Zureiq and al-Masalmeh were sanctioned, along with Assad family-affiliated individuals including his cousins, by the U.S., EU, and UK for their involvement in the production and export of the Captagon. However, al-Masalmeh was later killed after several attempts on his life by local factions due to his involvement in assassinating numerous opponents of the regime.
Hafo-Harfoush militia is another armed group led by two former opposition commanders Muhammad al-Masalmeh and Moayad Abdel-Rahman who -unlike other opposition groups- rejected the settlements and refused to be displaced to Northern Syria. They were, territorially, located in Daraa al-Balad neighborhoods until getting defeated by local factions supported by the 8th brigade in November 2022, for their links to ISIS cells, implication in assassinations against opposition figures based on revenge motives, and involvement in thuggery activities such as theft and imposing levies on locals. All of these security dynamics illustrate the overlap of security and war economy, notably the Captagon trade.
Alternative Policies: Addressing the Captagon Dilemma
Sanctions have not been effective in impelling the regime to make concrete concessions or changes such as in the case of the military intelligence in Daraa and similarly had no impact on the former opposition commanders, currently affiliated with the regime. The Arab engagement with the Syrian regime has not only failed to make progress in countering the Captagon trafficking, but the trafficking itself also increased after the normalization talks that led to the regime’s return to the Arab League in May, let alone the increasing technological capabilities of drug traffickers such as the use of drones.
For regional policy implication: First, Jordanian national security should be considered vital for regional security by Jordan’s international and Arab allies against the Iranian aspiration for a next domino after Lebanon, Iraq, Yemen, and Syria. Second, the assumption that the Syrian regime possesses the willingness and/or the capacity to counter the Captagon problem or disassociate from Iran should be reconsidered. Third, policy options should account for the interconnection of regime-affiliated security actors and Captagon trafficking, and the increasing capabilities of Captagon networks. The May statement by the Jordanian foreign minister on the prospect of taking military action to counter the Captagon threat in Syria and the three Jordanian airstrikes targeting drug smugglers and factories in May, August, and December, highlight an alternative policy based on coercive means that can and should be adopted in countering drug trafficking.
Given the lack of a comprehensive solution, three alternative policy scenarios can be illustrated:
- Strengthening state institutions: The interconnection between the regime and the smuggling networks, its use of the Captagon as a weapon, and the current inability to enforce security sector reform on the regime render the latter unreliable in countering the Captagon.
- Proactive targeting of Captagon networks: The Jordanian previous airstrikes were reactive in nature and limited in scale. A proactive strategy shall, rather, be focused on targeting the factories operating in different locations across Syria as well as the Captagon barons. Such a strategy requires U.S. and regional support in addition to coordination with Russia.
- Buffer zone: A demilitarization process in Southern Syria that necessarily requires a new status quo i.e. a new agreement with Russia and a new settlement that involves demilitarization. Such a scenario would prevent a potential spillover of the Gaza war to Southern Syria – which is, perhaps, in the interest of all parties involved. However, the technical challenges in enforcing and monitoring such settlement will not be easy to deal with.
Finally, the dynamics of the settlement in Daraa, its security repercussions, and its interconnection with the war economy can no longer be ignored, especially with the outstanding risk of spillover into the neighboring Sweida that has been gripped by a state of unrest since August.
The Source : Politics and Society Institute
Article link: https://bit.ly/3GZZjSc
Gaza War: The Responses of Syria’s Local Actors
Given Syria's involvement in the Arab-Israeli conflict since 1948, solidarity with Palestine has been a fundamental element within Syria's political culture. Regarding Syria's local actors’ stances on Gaza war (Syrian regime, Syrian opposition, “Hayat Tahrir al-Sham”, and “Syrian Democratic Forces”), while there is consensus in expressing solidarity with the Palestinian people in Gaza, their approaches to the war varied significantly in respective to their stances on Hamas, the “al-Aqsa flood” operation, and how they used the war in their different political strategies. These differences stemmed from a blend of ideological political identities on one hand and objective considerations related to their different relations with international and regional actors on the other. This article provides insight into the discourse projected by these actors on Gaza.
The Syrian regime has consistently propagated a narrative of resistance since the onset of the Gaza war, publishing official statements through its foreign ministry or speeches delivered by its prominent figures, notably Bashar al-Assad and his Foreign Minister, Faisal Mekdad. The regime praised the “al-Aqsa flood” operation as a “glorious achievement,” linking it to the October 1973 war due to its historical significance as a victory within the Syrian and Arab narrative.
Using the Gaza war in emotional mobilization of its popular incubator and its narrative of conspiracy, the regime associated the Israeli aggression with the ongoing struggle in Syria, holding Israel accountable for supporting the perpetrators of the drone attack on the Homs Military Academy on October 5th. This sentiment was further underscored by Mekdad when he criticized the stances of the United States and European states on Gaza accusing them of “Western deceit and open appetite for killing Arabs, including Palestinians.” In response to Israeli escalation of targeting various Iranian and regime sites in Syria, the regime continued to propagate a discourse centered on the right to defend sovereignty and reclaiming the Golan Heights within the 1967 borders.
By political means, the Syrian regime leveraged the regional atmosphere after the Gaza war to bolster its diplomatic activity within the Arab League and its bilateral diplomatic engagement with various Arab countries. While Assad advocated for halting the process of Arab-Israeli normalization during the extraordinary joint Arab Islamic summit on Gaza in November, the regime did not record formal reservation on any of the summit's resolution provisions, including having “normal relations with Israel,” a reservation upheld by Algeria, Iraq, and Tunisia (1).
This reflects the regime's alignment with the official and prominent Arab stance concerning the Israeli aggression on Gaza in formal diplomatic means, while concurrently maintaining a vehement anti-Israeli and anti-Western sentiment through its rhetoric, as a cornerstone of the “axis of resistance” led by Iran.
“Hayat Tahrir al-Sham” adopted a different narrative toward the “al-Aqsa flood” operation in comparison to jihadist groups - al-Qaeda and its branches - that advocated in their statements for jihad and targeting Western sites in Muslim countries. HTS's official rhetoric, expressed through statements by its “Syrian Salvation Government,” revolved around praising the operation carried out by Hamas, endorsing the Palestinian people's right of “the entire liberation of Palestinian land,” and calling on the “international community and Arab nations” to halt the Israeli aggression on Gaza after the Israeli targeting of Jabalia refugee camp. HTS’s call, in essence, mirrored a statement issued earlier by the Taliban government, which has been promoted as a “model” by prominent figures within HTS.
As it has been promoting itself as a moderate actor, the SSG’s Ministry of Media issued -ironically- a statement on press freedom and condemned the Israeli targeting of journalists regardless of their faith. This condemnation included Israeli violations of the targeting of journalist Wael al-Dahouh's family, the killing of journalist Sherin Abu Akel in Palestine, and the targeting of journalist Carmen Joukhadar in Lebanon.
At the same time, the jihadist element remained present in the speeches of HTS figures, notably Abdul Rahim Atoun, the head of its Fatwa Council. He said that the conflicts in both Syria and Palestine constitute a jihad that is an "obligation" upon every Muslim. This declaration was made during a symposium titled "From Idlib to Gaza... One Wound," organized by the SSG’s Ministry of Media. This highlights the tone difference in the technical statements and media discourses as well as the continuation of the jihadist ideological element within HTS's narrative.
Nevertheless, the primary objective of the symposium was to draw parallels between the Palestinian resistance against Israel and the Syrian struggle against the regime. The focus was on highlighting the similarities in crimes committed against the Syrian and Palestinian people, by the Assad regime and Israel respectively. This narrative resonated with SSG’s official statement, which regarded Palestinian resistance as an inspiring model for the struggle against the Syrian regime. A narrative aligns with HTS's efforts to project a national-Islamist image at the expense of its former Jihadist one.
As for the Syrian Opposition, the Syrian Negotiation Commission, the Syrian National Coalition, and the Syrian Interim Government expressed solidarity with Gaza, particularly following the bombing of al-Maamadani Hospital. Both the statements from the Negotiations Committee and the National Coalition condemned the crimes committed by Israel and emphasized the significance of the Arab Peace Initiative (2002), rejecting the forced displacement of Gaza residents. Simultaneously, the Interim Government condemned the crimes of the Israeli occupation and declared a three-day national mourning in its controlled areas.
Regarding their stance on Hamas or “al-Aqsa flood,” there hasn’t been any official statement or position issued on the matters, given the challenge of attaining a unified stance within the opposition due to the varying and sometimes conflicting positions toward Hamas, driven by ideological or political reasons related to Hamas's stance on the Syrian regime or Iran. Let alone the objective considerations related to the opposition’s political relations with international and regional actors.
As for the “Syrian Democratic Forces,” the SDF-affiliated “Syrian Democratic Council,” issued a statement condemning the targeting of civilians in Gaza, particularly the al-Maamadani Hospital, taking into consideration the pro-Palestinian sentiment among Syrians. The statement made reference to the “right of the Palestinian people to self-determination,” in line with SDF’s claim of the “Autonomous Administration” in Northeastern Syria. On Hamas, the head of the SDF, Mazlum Kobane, condemned it, yet expressed concerns over the Israeli objective to eradicate Hamas because of the potential spillover effects of such eradication.
The response of local actors in Syria to the Gaza conflict varied significantly in their level of engagement, political stances, and the use of the war in their narratives. There has been notable and active engagement by the regime and HTS, moderate engagement from the opposition, and cautious one from the SDF. The regime leveraged the Gaza war in emotional mobilization within its popular incubator as a cornerstone of the resistance axis by endorsing Hamas. Simultaneously, the regime has politically capitalized on the regional atmosphere to strengthen its diplomatic presence within Arab politics. HTS has also used the war in emotional mobilization in Idlib and in its rebranding process as a local actor endorsing Hamas as a model. In contrast, the opposition limited its response to humanitarian solidarity with Gaza, refraining from issuing an official stance on Hamas. The SDF pursued minimal engagement with Gaza and was the only actor to take an anti-Hamas stance along with fearing the repercussions of the war.
Finally, the result of the war on Gaza, will have impact on these actors, particularly for HTS and SDF, at least in terms of boosting their confidence to survive as semi-state actors in case Hamas survives the Israeli military campaign or diminishing that confidence in case Israel manage to eradicate Hamas.
([1]) This stance followed the regime's prior formal reservation on “any wording that could be interpreted to equalize between the Israeli occupier and the Palestinian people living under occupation,” in the resolution of the extraordinary ministerial session of the Arab League on Gaza in October, akin to reservations expressed by Iraq, Libya, Algeria, as well as Tunisia which objected to the resolution entirely, advocating for “the right of the Palestinian people to establish their independent state on all of the territory of Palestine.”
An invitation to submit a research paper to the second research conference of Omran Center titled: Early Recovery in Syria: Realities and Future Perspectives
Early recovery in Syria stands out as one of the most significant variables that has started to take shape in recent years. There are indications of varying dynamics in early recovery in the current areas of influence, which are distinct in terms of local actors, needs, resources, and capabilities, as well as variations in local, regional, and international approaches to this variable. In this context, the Omran Center for Strategic Studies, in collaboration with Mardin Artuklu University, is organizing its second research conference titled “Early Recovery in Syria: Realities and Future Perspectives”.
Therefore, we announce the commencement of receiving research proposals for participation in the conference in Arabic, English and Turkish. The deadline for submitting research proposals is January 31, 2023.
The conference is scheduled for May 17-18, 2024.
For more details:
- Main Themes and Subscription Criteria: https://bit.ly/47N6clq
- Conference Background Paper: https://bit.ly/47Jap9A
- Submission Link: https://bit.ly/3Gf1rFg
Military Field Court: Nullification and a No Change Approach
On September 3, 2023, Bashar al-Assad announced Legislative Decree 32 of 2023(1), which nullified Legislative Decree 109 of 1968 and its subsequent amendments. Which eventually had established the Military Field Court(2). With this new decree, all ongoing cases will be transferred to the military judiciary, where they will be prosecuted under the Penal Code and Military Procedure and its amendments(3).
The Military Field Court was initially set up in the aftermath of the Six-Day War of 1967. Its primary purpose was to address crimes that fell under the jurisdiction of military courts during times of war or military operations. Later, its scope was broadened by Hafez al-Assad through Legislative Decree 32 of 1980, allowing it to hear cases during "internal unrest" and thereby permitting civilians to be tried in this court.
It's crucial to note that this court does not meet basic litigation standards. It did not adhere to the principles and procedures outlined in existing legislation. Furthermore, its rulings, including death sentences, were final and not open to appeal. Death sentences required ratification from the head of state, while other sentences were approved by the Minister of Defense.
Historically, the court has been a tool for suppressing Syrian society. This was evident during the 1980s(4), and became even more pronounced after 2011. The security services frequently referred detainees to this court, where many faced the death penalty. Others were sent to “Sednayah Military Prison”, where they were systematically tortured to death(5) .
Despite the court's abolition, the situation will not change significantly. The security services still hold sway over the assessment and categorization of crimes. Over 100,000 detainees and forcibly disappeared individuals remain in the regime's prisons(6) . This suggests that changing the judicial tool does not necessarily alter the regime's behavior. The core issue lies in the fact that there is a governance defect in the military judiciary as a whole(7) . which is summarized by its connection to the executive authority represented by the Ministry of Defense and the connection of its officers to the security services. Moreover, the court has been a hub for financial extortion against detainees' families, generating millions of dollars through corrupt networks(8) .
Furthermore, the challenge of trying civilians in military courts persists. One of Syria's primary issues is the lack of an independent judiciary, both military and civilian. Bashar al-Assad, as the “President of the Republic,” presides over the Supreme Judicial Council, as per Article 133 of the 2012 Constitution(9).
The decision to abolish the court appears influenced by external pressures rather than domestic concerns. The Assad regime seems to be diverting international attention from human rights issues, state restructuring, and accountability. The regime is likely to continue with symbolic gestures, such as issuing new amnesty decrees, reducing military presence on public roads and dismissal of a number of conscripts and reserve personnel from the army. These actions are seen as superficial attempts to appease the international community amidst the regime's growing isolation and economic crisis.
The court's abolition is also seen as a move to pre-empt international legal actions against the Assad regime for torture crimes. This comes ahead of the “International Court of Justice's” hearings on the lawsuit filed by Canada and the Netherlands against the regime(10). The decision is also linked to the Arab initiative and the step-by-step approach, especially concerning refugees' legal and security concerns.
A significant aspect of this decision is the regime's attempt to distance itself from the Military Field Court's actions, especially since its reactivation in 2011. In accordance with paragraph (a) of Article 8 from the decree that established the court, death sentences required ratification from the head of state. This means every death sentence since 2000 has been directly approved by Bashar al-Assad.
The annulment of the military field court decree doesn't negate it’s on the ground application automatically. It's tied to other procedures, and mere superficial changes at the top aren't sufficient. Resorting to the military judiciary often leads to further repression due to significant loopholes. This judiciary's laws and its consistent use serve as intimidation tools.
The regime's decision to dissolve the court can be attributed to its strategy of handling enforced disappearances and murders. By operating within this exceptional judiciary and indirectly sending detainees to “Sednayah military prison”, this helps the regime circumvent the UN General Assembly (UNGA)’s decision to form an international mechanism to reveal the fate of missing persons in Syria. This move coincides with Canadian and Dutch efforts to hold the regime accountable at the International Court of Justice for violating the convention against Torture, which was ratified by the regime in 2004.
Previously the Assad regime abolished the state of emergency and the State Security Court in 2011(11). By 2012, they introduced the Anti-Terrorism Law and established the “Terrorism Cases Court”(12) . However, these changes didn't alter the regime's oppressive tactics. Instead, they intensified their crackdown through various courts, including military, field, and civilian ones. With the “Military Field Court's” dissolution, its alternative is already in place.
Genuine change in Syria isn't about switching litigation tools. It hinges on three unavailable criteria: judiciary independence, assigning case types to the Attorney General instead of security services, and a shift from emergency law dynamics. The distinction between judicial tools is merely administrative.
Real change in Syria requires a conducive political environment, an independent judiciary, and robust constitutional institutions that enforce the law. Local civil bodies must oversee the change process and safeguard citizens' rights. Without transparency and laws granting access to information, assessing change remains impossible, especially with the regime's secrecy around detainees and the missing.
For legal reform in Syria, two primary requirements stand out: First: abolishing the laws from which security agencies feed. Second: legally curbing the violations of security agencies, especially arbitrary detention, and torture, which are tools to silence and instill fear in citizens, their violations can be curbed through laws combating arbitrary detention in its three types, ensuring the foundations and rules of a fair trial, and combating torture.
In conclusion, the regime’s changing of the sole leadership system will remain symbolic and evasive captive to formalism, blackmail, and evasion, which has been its practice throughout the Baath era. Genuine change requires a political climate that involves all actors. While the regime might present this move (Abolition of the field court) as an extension of the Arab initiative or a political process step, it's likely a superficial response to growing internal unrest, particularly in Suwayda and southern Syria.
Human rights and civil society organizations must critically assess these developments. Political entities should push international players totem pressure the regime and its allies to address the fate of the missing, ensure a safe environment for Syrians' return, and earnestly participate in the political process, with Resolution 2254 at the forefront.
([1]) “Legislative Decree No. 32”, Sana, Publication date: Sep 03, 2023, Link: https://bit.ly/48AmAXB
([2]) “Bashar al-Assad ends the system of military field courts”, The new Arab, Publication date: Sep 03, 2023, Link: https://bit.ly/46i3Jiy
([3]) “The Penal Code and Military Procedure”, The Syrian Parliament, Publication date: Mar 13, 1950, Link: https://bit.ly/3Lh0EUh
([4]) “The Muslim Brotherhood Uprising in Syria (1979-1982) which comprised the Hama massacre”, EUAA, Publication date: September 2020, Link: https://bit.ly/3LKVD9V
([5]) “An Instrument of Death and Disappearance: How the Syrian Regime Uses Military Field Courts Against Activists and Dissidents” SNHR, Publication date: Sep 12, 2023, Link: https://bit.ly/46BuVZ4
([6]) SNHR’s 12th Annual Report on Enforced Disappearance in Syria”, SNHR, Publication date: Aug 30, 2023, Link: https://bit.ly/46z6w6
([7]) “Changing the Security Sector in Syria”, Omran Center for Strategic Studies, Publication date: Oct 23, 2017, Link: https://bit.ly/45jogSp
([8]) “Families of Syrian prisoners and missing persons 'paid $900 million' to find out the fate of their children”, BBC, Publication date: Sep 14, 2023, Link: https://bit.ly/3EZXbJ4
([9]) “Syrian Arab Republic 2012”, Constitute project, Publication date: Feb 27, 2012, Link: https://bit.ly/48Giihe
([10]) Application of the Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment (Canada and the Netherlands v. Syrian Arab Republic)”, International Court of Justice, Publication date: July 15, 2023, Link: https://bit.ly/45irIwH
([11])“Syria announces lifting of state of emergency and cancellation of Supreme State Security Court”, the world of the homeland, Publication date: Apr 10, 2011, Link: https://bit.ly/3LJUv6l
([12])“Law 22 of 2012 establishes a Damascus-based terrorism case court”, The Syrian Parliament, Publication date: July 26, 1950, Link: https://bit.ly/3RrxSqP