Events
Navvar Saban | Will Syrian regime launch new battles in opposition regions?
Navar Saban, expert in military situation at the Omran Center for Strategic Studies in Istanbul talking with Enab Baladi about the recent military developments in southern Idlib and mainly near the M4 and the possible scenario for the M4 agreement.
Briefing on Latest Developments in Idlib
I. Introduction
Both Turkey and Russia agreed to a ceasefire in Idlib starting at midnight on March 5th,2020. At the time, both sides saw this agreement as representing the least worst case scenario to preserve its interests on the ground and prevent further escalation between different actors. On one side, the Russians and regime forces heavily escalated systematic attacks on civilians and basic infrastructures driving over 1.1 million civilians towards the Turkish borders, hence putting pressure on Turkey and indirectly on Europe. The regime aided by the Russian airforce regained control over vacated villages in the Idlib province and was advancing on more heavily populated areas. On the other hand, after several attacks by the regime against Turkish military forces, the Turkish army heavily escalated its presence and equipment in southern Idlib and broke away with previously agreed “rules of engagement” by attacking regime and Iranian backed forces to stop its advance and prevent further displacement of the civilian population. The agreement hence, was a temporary freeze of operations by all sides. It included the following core elements:
• A ceasefire from the morning of March 6, 2020 along the frontline.
Regime artillery continued to target several locations in the vicinity of the new buffer zone north of the M4, Sources confirmed that 56 violations done by the Regime March 6 to March 31 of the same month.
• Establishing a security corridor six kilometers north and six kilometers south of the main international highway in Idlib "M4," which links the cities controlled by the Syrian Regime in Aleppo and Lattakia, and open an internal crossing between the Regime and Opposition held areas.
Because of the new Corona (COVID19) and the fear of an outbreak of the disease, the interm government in Idlib decided to close all the internal and external borders in Idlib and western Aleppo, but in April 17, 2020 HTS announced its intention to open a commercial crossing with the regime that links both Saraqib and Sarmin, which met with widespread disapproval among civilians and demonstrated near Sarmin objecting to the matter.
• Joint Russian-Turkish patrols to be deployed along the M4 road, starting March 15.
As of April 18, 2020, no full joint patrols were conducted for the entire route for security and logistical reasons. A group of civilians built tents along parts of the road, refusing the passage of Russian patrols, while some military factions took advantage of the situation and worked to further destabilize the security situation. Sources of the Information Unit at Omran Center confirmed that these factions are affiliated with HTS. HTS has been taking steps to indirectly create problems and then present itself as part of the solution in an attempt to legitimize its presence in any future security architecture.
II. Updated map of control in Idlib and its surrounding areas
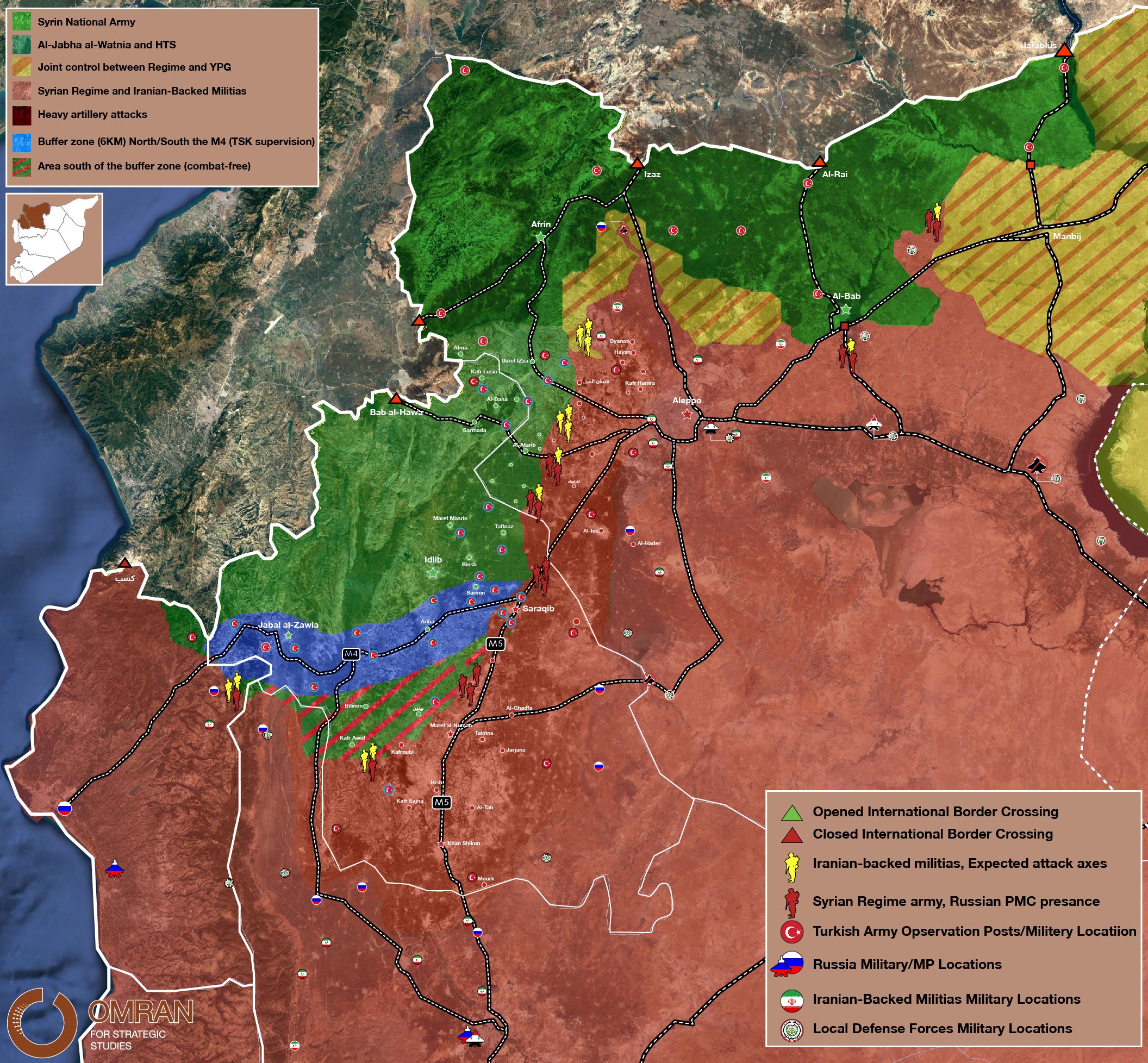
Updated Control map of Control in Idlib by Information Unit in Omran Centre – 18 April 2020
III. Major developments of the "M4" agreement
A. Turkey’s four current goals
1. Preventing the threat of Corona (COVID19) especially in IDP camps. This can be observed through the strict measures at border crossings, reducing to the maximum interactions with locals, pushing IHH organization to improve its plans, as well as high engagement by AFAD.
2. Increasing Turkish Military posts defense and sending more vehicles and soldiers in the past weeks to establish new posts in Jabal al-Zawyie and al-Ghab Plain.
3. Opposition factions: restructuring National Liberation Front (NLF) by arresting and demoting corrupt commanders, requesting from each faction to call fighters to training camps to compare numbers of fighters and ending any possible connection between groups and other countries in order to ensure order and containment.
4. The M4 agreement with Russia: Turkey is pushing hard for the joint patrols on M4, which has been facing obstacles through sit-in demonstrations by some local actors with direct threats from HTS sub-entities. Turkey is carefully trying to end this situation without using force and by negotiating with the locals. Resolving this situation is a top priority before May in order to prevent any Russian military acts.
B. Positions of local and international actors in Idlib
1. The joint patrols along the M4 highway is Russia’s main priority. There were little if any statements by Russia calling upon Turkey to implement the agreement during February-April, unlike early January. Russia is focusing on dealing with the Corona pandemic and countering increased ISIS threats in eastern Homs, Daraa, and Deir Ezzor.
2. Several news sources indicated that the UAE is pushing the regime to launch a new attack on Idlib and giving promises to fund such an operation. Russia asked the regime not to launch any attack after regime unilaterally and without consulting the Russians sent reinforcements to Idlib.
3. The presence of Iranian-backed militias in Idlib is less than other areas in Syria. However, for Iran to establish a foothold it needs to send more fighters and to launch a limited attack. IRGC-affiliated militias are present in Kafrnabel but are not the main attacking force. Once again, Iran is using its old methods: initial expansion in new areas followed by provision of basic services for local communities.
4. The recent Turkish/Russian agreement put further pressure on HTS by pushing it to re-share power in Idlib with NLF. Furthermore, the Turkish heavy military presence and the deal with the Russians is making Jihadist inside HTS angry and pushing them to breakout. This can be seen in the resignation of Abu Malek al-Talli, and the sit-in protests on the M4 by offshoot members of HTS.
5. HTS has been taking steps to restructure itself, and started by forming 3 new divisions and mixing the hardcore jihadist groups with other less radical members under the leadership of local members.
6. HTS seems to attempts to contain and weaken the more extreme elements within its ranks in order to reduce the risks of possible defections and ensure a future smooth transition from a Jihadi group to a political Islamist group. It is also taking steps to continue its local control over governing bodies such as the Salvation Government.
IV. Future directions
1. There will most likely not be a major regime attack in the near future and even from the opposition side too.
2. May is the month of action for the Turkish sides in order to get ready of the difficult situation surroundings the M4 agreement.
3. The area is witnessing more Iranian-backed militias activities, those activities will increase I. The future in different levels (Economic, Security and military)
4. COVID19 is not the main concern for the local and international actors in Idlib; positive reading is confirmed from the Opposition held areas in Idlib.




