Events
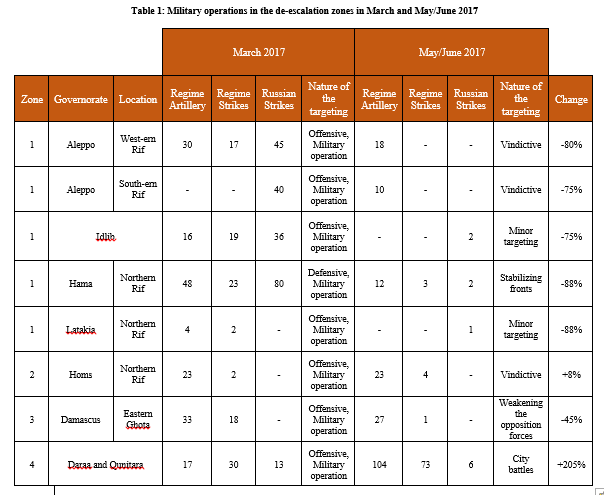
Al-Qaeda Affiliate and Ahrar al-Sham Compete for Control in Idlib
"This special report was published byMiddle East Institute , in collaboration with Omran for Strategic Studies, andOPC- Orient Policy Center"
Idlib is currently the site of increasing competition between the two most dominant armed coalitions, the al-Qaeda-linked Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (H.T.S.) and Ahrar al-Sham. The province has witnessed limited airstrikes since a de-escalation agreement, which came into effect on May 5, was brokered by Russia, Turkey, and Iran at the Astana talks. Idlib was one of four areas labeled as a de-escalation zone.
The agreement has, however, prompted a contest between H.T.S. and Ahrar al-Sham, with both groups vying to increase their influence and control new areas. The competition between them has three dimensions: military, economic, and social.
For strategic, economic, and military reasons, H.T.S. has focused efforts on controlling vital towns, specifically along the Syrian-Turkish border on the western side of the province. H.T.S. fighters that shifted to the region from losses in Aleppo and Homs were deployed carefully in areas where the al-Qaeda affiliate wanted to increase influence, particularly along the northwestern border.
The “smuggling” route along the border from Harem to Darkoush is totally controlled by H.T.S., which uses it to transport oil and other goods. The mountainous nature of the area and its many caves also allow H.T.S. to thwart any attack or attempts by Ahrar or any other group to assert control in those territories.
Though H.T.S. controls military bases in the area, such as Taftanaz, to the northeast of Idlib, and Abu Dhour, southeast of Idlib, the group faces challenges in governance. Lacking communal support and strong governing skills, H.T.S. can’t fully control major cities like Idlib, Maarat al-Noaman, and Saraqib. Even in smaller towns like Kafranbel, where civil society has been active, H.T.S. has also failed to maintain a tight grip.
The experience of Maarat al-Noaman is an example of how local communities have played a major role in confronting H.T.S. Since February 2016, civil society has actively mobilized against al-Qaeda’s presence, first against Jabhat al-Nusra, as they were called at the time, and later against present-day H.T.S. The group was unable to control the city or defeat armed opposition groups largely due to the local community’s support for the armed groups. “It is not the armed groups there that protected civil society and the local community, it’s the community that prevented H.T.S. from defeating the armed opposition inside the city,” said Basel al-Junaidy, director of Orient Policy Center.
The only large city H.T.S. has been able to control is Jisr al-Shughour, in part because the armed groups surrounding the city are loyal to Abu Jaber, the former leader of Ahrar al-Sham who defected to H.T.S. earlier this year.
Following increasing pressure from Turkey to protect its borders, H.T.S. delegated to Ahrar al-Sham control over parts of the northwestern border near the town of Salqin. However, H.T.S. still enjoys influence there, and Ahrar still needs H.T.S. approval to appoint the leader of the group assigned to watch the border in that area.
Yet the current map could also be misleading. There are areas where H.T.S. has presence, but struggles to maintain control, and there are areas where it does not yet have a presence, but could expand power if threatened. For example, the main border crossing between Idlib and Turkey is Bab al-Hawa. It is controlled by Ahrar al-Sham, but H.T.S. controls the route leading to the crossing through several checkpoints, and has the capability to attack the border crossing and seize control at will.
In the north, Sarmada is becoming the economic capital of Idlib. H.T.S. controls most of the decision-making there with regards to regulations like money transfers, the exchange rate, and the prices of commodities like metal and oil. On the other hand, H.T.S. is weakest in southern Idlib, from the borders of the Hama province to Ariha, the social base for Ahrar al-Sham.
H.T.S. governs through its General Directorate of Services, which competes with several other entities to provide services. These competitors include Ahrar al-Sham’s Commission of Services, local councils under the umbrella of the opposition interim government, independent local councils, and civil society organizations. A recent study conducted by the Omran Center shows that there are 156 local councils in the province of Idlib; 81 of them are in areas where H.T.S. has a strong presence. As highlighted above, however, H.T.S. doesn’t enjoy equal control over all of these councils. While in some instances the group has comprised whole councils—as in Harem, Darkoush, and Salqin—in other councils, H.T.S. is only able to influence some members.
Due to the de-escalation zones agreement, H.T.S. currently finds itself in a challenging position. When the Nusra Front established its presence in Syria, it promoted itself as the protector of the people. Escalating violence helped the group gain legitimacy and sympathy, and many armed groups found a strong ally in the al-Qaeda affiliate as battles raged against the regime. As front lines become quieter, H.T.S. is beginning to lose its appeal.
The H.T.S. alliance also faces internal threats. The dynamics are changing between Nusra and the Nour al-Din al-Zenki movement, the second largest component of H.T.S. On June 2, Hussam al-Atrash, a senior leader of Zenki, tweeted that areas out regime control should be handed over to the opposition interim government, and all armed groups should dissolve. Atrash justified his suggestion as the only way for the Sunni armed opposition forces to survive. The comments irritated H.T.S. leadership, which referred Atrash to the H.T.S. judiciary. The tweets disappeared shortly thereafter.
Following that incident, H.T.S. banned all fighters from mentioning any subgroup names, like Zenki, to enforce unity. However, it is unlikely that H.T.S. will be able to maintain long-term enforcement. No opposition military alliance has been able to survive throughout the Syrian conflict, and subgroups continue to migrate from one umbrella to another for tactical reasons, seeking military protection and/or new funding opportunities.
While H.T.S. faces these internal and external challenges, it is also evolving. Its leadership clearly realized the importance of building stronger connections with local communities in order to compete with Ahrar al-Sham. H.T.S. adopted new tactics in governing. Instead of appointing foreigners or military leaders, H.T.S. has appointed local civilians as its representatives in most of the towns under its control in Idlib.
H.T.S. and Ahrar will continue to compete in governance and service provision, which is key to building loyalty, increasing influence, and widening public support. The groups are also cautiously following regional and international developments as they prepare for different scenarios. If the de-escalation agreement collapses or an external force intervenes in Idlib, all dynamics will certainly change. Ahrar and H.T.S. might confront each other, become allies, or re-shuffle their respective coalitions. The situation in Idlib is far from stable.
De-escalation Zones: A Cloak to Refocus on the East
Executive Summary
-
The de-escalation zones from the latest Astana meeting on Syria aimed to freeze the conflict on the western fronts in order to deploy the regime and its allies’ forces to prevent a total loss of the eastern territories to the American-led Kurds and opposition forces. Securing Tehran-Baghdad-Damascus-Beirut free passage is strategically more important compared to Idlib or Ghota at the moment.
-
The agreement was largely observed by all parties (Russia, Turkey, and Iran) and resulted in an immediate reduction in military operations in the selected zones. Compared to the level of operations in March 2017, May/June 2017 witnessed an 80% reduction in western Rif of Aleppo, 75% in Eastern Rif of Aleppo, 97% in Idlib, 88% in Hama, 80% in Latakia, and 45% in Ghota of Damascus. There was a slight rise in military operations in Homs (8%) and a radical increase in Daraa (205%) but that increase was mainly attributed to vindictive offenses like in Homs, or tactical deterrence to the opposition as in Daraa’s al-Manshia district.
-
The latest Geneva talks ended with no significant outcome, probably in anticipation of settling the current competition over Raqqa and Dir Ezzor. It is unlikely for Geneva to restore its significance before stabilizing the military situation and before the US and Russia move towards a serious political settlement.
-
It is still too early to determine if the de-escalation zones can serve as a basis for a Russian strategy to stabilize the situation on the ground and foster an environment conducive to a political solution. The outcome of the battles on the ground in the East and the sustainability of ceasefire in the West will determine such an outcome. Neither easy nor quick dominance in the East is in sight for either side. Particularly because of the proxy nature of the operations, lack of cohesion between the participating forces, and unprofessionalism of the local forces aligned with the Americans (Kurds and opposition forces) and Russians (tribal forces and Fifth Corps).
-
Nor will there be a clam west, as HTS (al-Nusra coalition) will aim to expand and exhaust the moderate forces with potential reactions from the latter. Accelerated foreign contact, including by the Russians, with the Local Administration Councils (LACs) in the de-escalation zones is expected in order to secure influence during the transition period.
-
This paper argues that the political opposition should unite its negotiations delegations and increase its capacity and legitimacy. The military opposition should support the political process and provide views on its role in the future. The LACs should focus on their service delivery role and improve their capacity to meet the tasks of reconstruction and return of refugees. More important for the Local Councils is to avoid local politicization and alignment with either regional or global actors in order to protect their neutrality as guarantors of a stable future for Syria.
-
The US and EU should support forming a united negotiation delegation for the opposition as a political solution might be looming on the horizon, especially after the situation in a post-ISIS Raqqa and Dir Ezzor settles down. Notably, engagement in Russian-led Astana talks is important to develop critical ideas on a US-EU/Russia cooperation in the transitional period.
-
Russia should support the legitimacy of the opposition delegations and refrain from undermining their efforts to effectively represent their Syrian constituency. More strategically, Russia should approach to the Local Councils, support their professional service delivery, and coordinate with their EU sponsors to assure fruitful cooperation in preserving their role in the future.
Map No. (1) Russian Proposal for Safe Zones
Introduction
The latest two peace negotiation rounds on Syria ended with postponing the serious discussions until after the dust settles in the east of Syria. The Astana meeting in Kazakhstan produced an agreement on de-escalation zones, supported by Russia, Turkey, and Iran and opposed by Syrian opposition representatives. Not surprisingly, the Geneva talks did not break the low ceiling of expectations and ended where it started. The de-escalation zones serve Russian interests on many fronts, the most important of which is freezing the West “hot spots” (Idlib, Hama and Homs) to focus on the eastern front where Russia aims to disturb the American-led operations to recapture Raqqa and Dir Ezzor on the border with Iraq. The post-ISIS-controlled areas constitute the next battleground and are, to a large extent, the determinant of the final balance of power among all parties in future negotiations. While the eastern fronts will be fluid and hardly stable, the western fronts will not be calm either.
A few weeks before signing the agreement in Astana, there was an immediate reduction in military operations in the selected zones. Compared to the level of operations in March 2017, May witnessed an 80% reduction in western Rif of Aleppo, 75% in Eastern Rif of Aleppo, 97% in Idlib, 88% in Hama, 80% in Latakia, and 45% in Ghota of Damascus, according to the information unit at Omran Center. Some exceptions to the main reduction in hostilities were observed in Homs (8%) and Daraa (205%), with some vindictive offenses in Homs and tactical deterrence of the opposition forces occurred in Daraa.
The opposition forces (i.e., HTS, Ahrar al-Sham, and some MOC-affiliated militias) in late April has occupied al-Manshiya district in southern-Daraa and threaten to advance further into the regime controlled areas in Daraa; therefore, the regime aims to stop their advancement by redeploying forces from around Damascus after solving the problem of Qaboon and Barza cities. The Ghaith al-Dalla forces of the fourth division have joined the Shite militias in the south (Hizbullah, Iranian Revolutionary Guard IRG, and the Fatimioun brigades) to stop the opposition advancement beyond al-Manshiya using aggressive, rather tactical, deterrence offenses. (see Table 1 for more details).
This paper addresses the context of the de-escalation zones and provides an overview of the situation in all of the active fronts in the east and west of Syria. It also includes three sets of recommendations to the Syrian opposition (Political, Military, and LACs), as well as recommendations to 1) the US and the EU and 2) Russia.
The analysis concludes that both the Russians and Americans rely on forces that lack central coordination, professionalism, and discipline. Such characteristics weaken control over the operations, hence making it almost impossible to predict their outcome and trajectory. This turbulent and cloudy situation will dominate for an extended period, given the absence of a political framework to accommodate ISIS members after their organization collapses and they escape to new havens. In turn, the western fronts will be busy with HTS attempts to expand geographically and weaken the moderate opposition politically. There also will be an international and regional race to influence the LACs, considered the black horse in any future efforts for stabilization in the de-escalation zones through humanitarian aid, the management of the return of refugees, and reconstruction shall security guarantees are offered.
Information Support Unit, Omran Centre for Strategic Studies
De-escalation in the West, Escalation in the East
While attention is refocused on Raqqa and Dir Ezzor in the east of Syria, the latest agreement signed in Astana helps to freeze the western fronts in order to reallocate resources and concentrate forces for the upcoming battles in the East. The fall of both Raqqa and Dir Ezzor to America’s proxies limits Damascus’ control over the borders, cuts Iranian routes from Tehran to Beirut through Baghdad and Damascus, and empowers America’s grip over both Iraq and Syria.
The protracted war has exhausted the regime forces and devastated its capabilities, and the long line of active fronts in the West has distracted its allies’ attention to the slow developments in the East. The advancement of the Syrian Democratic Forces towards Raqqa and the Southern Front opposition forces towards Dir Ezzor alerted the regime to a near loss of the borders with Iraq. There was a severe need to reallocate the regime from Idlib and Homs, where they can revert to them later, to the eastern fronts, where it is more pressing to secure a foothold.
The new battle needs more manpower and expertise. For these, the Russians and Iranians rushed to organize the tribal forces and integrate them into the Fifth Corps under Russian command. Hizbullah has recently, and rather quickly, given its positions in the South to the Russians and its positions on the Syrian-Lebanese borders to the Lebanese Army; Hizbullah redeployed their forces close to Palmyra. The latest efforts of Hizbullah serve two purposes: 1) to release tension with Israel and hence avert an Israeli attack on Hizbullah inside Syria, and 2) to use its shrinking manpower more strategically to protect its supply line from Tehran.
Recent news coming from Syria was dominated by the American alliance strikes against a military convoy for the Shia militias approaching al-Tanaf crossing, which was captured recently by the American-led forces. Days later, and in a sign of resolve, the alliance forces air-dropped brochures that “advises” the Shia militias to refrain from further approaching opposition-controlled areas. Russia might have to negotiate with the Americans to secure a place on the borders for the Iranians, but that will come at a high price and only if the Russians succeed in interrupting the connection between the Kurds coming from the North and the Opposition groups advancing from the South.
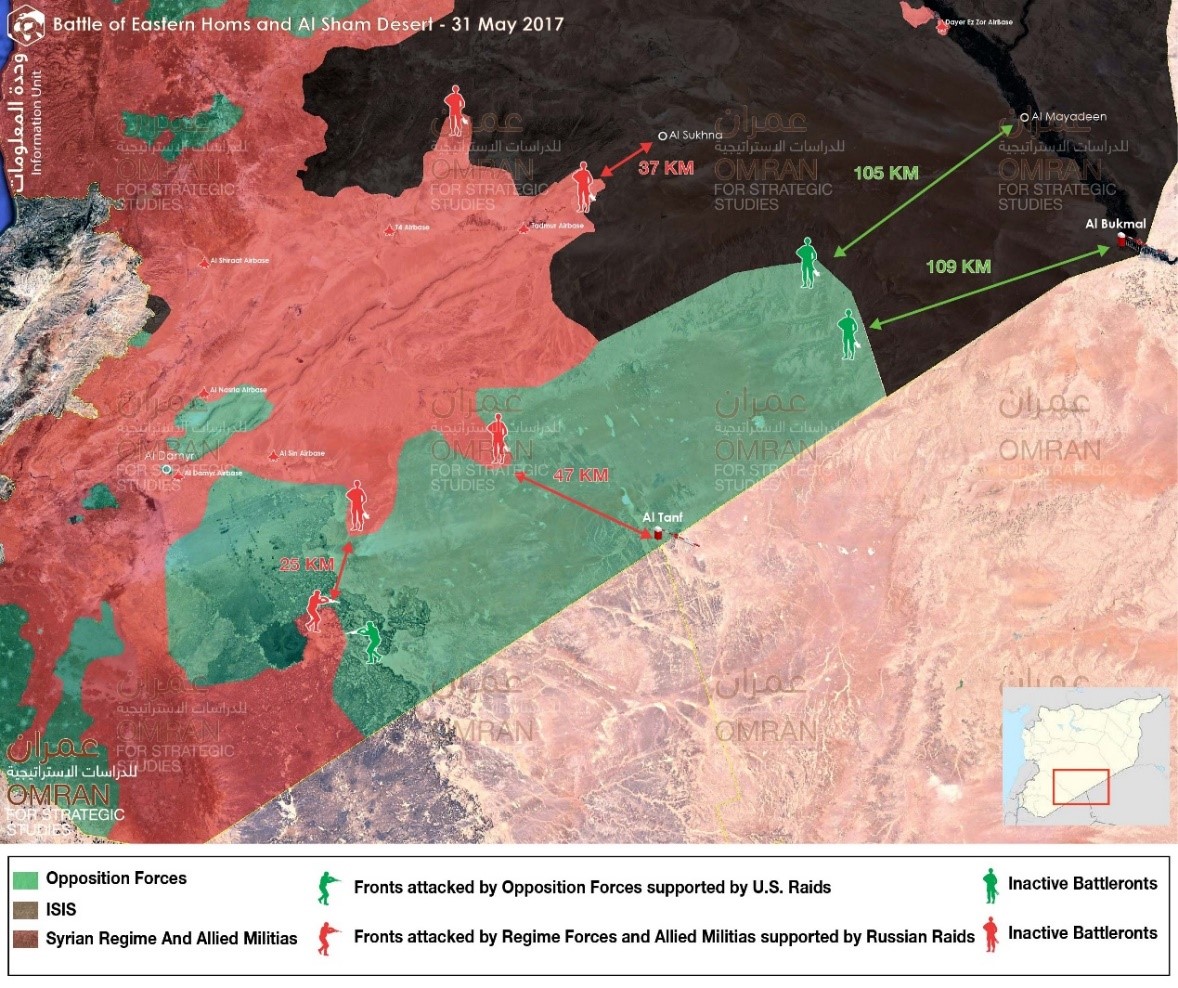 Map No. (2) Battle of Eastern Homs and Al Sham Desert- 31 May 2017
Map No. (2) Battle of Eastern Homs and Al Sham Desert- 31 May 2017
This context shows that the de-escalation zone agreement was neither a Russian secret plan to divide Syria, nor a Russian trap for the U.S. and its allied groups. It actually reflects a pressing need for Russia to freeze the conflict for six to twelve months in the areas that have no strategic urgency, such as Ghota in the South, where Israel is concerned, or where in-fighting and Turkish influence will shape the situation in a less costly way compared to a direct intervention, like in Idlib. At this moment, Dir Ezzor is strategically more important than Idlib, and Nura is less of a threat compared to losing the borders with Iraq to the Americans.
Controlling the borders will change many equations for the regime and its allies: it will challenge its attempts to reclaim control over all of the Syrian territories; it will block the Iranian routes to Hizbullah; and it will give Americans the upper hand in both Syria and Iraq. Russians have tried to avoid confrontations with the Americans since their intervention in 2015, and such a scenario with American-proxy domination of the East and South might lead to undesirable tensions. More important, it is possible that at any moment the pressure of American proxies from the East and South on the regime areas will reverse the military vulnerability that Russia has successfully avoided in Syria so far. Consequentially, it is possible that Russia will be forced to accept a settlement that is not optimal to its interests.
The details of the agreement promise a successful implementation, but the absence of any follow-up or enforcement mechanisms make any euphoria disappear. There are sections of the agreement on international forces and monitoring mechanisms, guarantors, humanitarian access, refugees return, and reconstruction—all dependent on moderate forces restoring security and fighting terrorist groups. The possibility that moderates will be blamed for future acts of terrorists may cause rifts. The moderates will have to either essentially self-destruct by intensifying the in-fighting or face the threat of invasion or bombing by the Russians and the regime. The latest coalitions of HTS (al-Nusra coalition) will not be weakened or reversed before reaching a comprehensive political solution that could encourage small groups and individuals to defect and motivate the militia as an overall body to engage in a national Syrian military and political effort that meets its expectations.
Within the context, rather than the text, of the agreement, Turkey has agreed with Russia to deal with HTS in Idlib, an arduous task. Without a political settlement, Turkey will find itself facing increasingly disgruntled military groups that have the capacity to threaten the depth of the Turkey. There is little in the agreement that justifies the Turkish presence or its acceptance of the Iranian guarantees. However, given the Turkish sensitivities towards any expansion of the Syrian Democratic Forces, which is dominated by the YPG and its PKK connections, Turkish cooperation with Russia becomes less questionable. The Turks have an interest in depriving the Kurds from having a seat at the negotiating table to determine Syria’s future. Moreover, with current challenges in Turkish-American relations, any increase in U.S. presence in both Syria and Iraq potentially diminish the regional influence of Turkey. The Turks find themselves implicitly allying with the Russians and Iranians, against the Kurds and the Americans.
The US and the EU did not pay attention to the Astana conference from the beginning in order to avoid reducing the importance of Geneva to Russian-led talks and to comply with their Iran marginalization policy. Militarily, The Americans did not respond to Aleppo’s fall or Idlib’s suffer because there were considered out of their strategic influence zones. Alternatively, Americans invested heavily in the Kurds and the southern groups in cooperation with the UK and Jordan in order to capture ISIS-dominated areas in the East. That will not only increase the areas under their control but also will increase the US legitimacy as successful forces in fighting terrorism. The US hope that strategy will create a new situation that will force the regime and its allies to negotiate seriously, by American terms, in Geneva or otherwise. In the meanwhile, the Europeans did not break their silence on Astana either. The EU focuses only on Geneva and is suspicious of Russia’s efforts. The Russians failed to buy their support to Astana despite the incentives inserted in the agreement by promising the return of refugees and reconstruction.
Indetermination in the East, and slow fire in the West
Against the clarity of the parties’ plans, the realities on the ground might tell a different story. Looking more closely at the formation of the competing forces racing towards Raqqa and Dir Ezzor, it appears that they are neither professional nor disciplined nor coherent in their composition or end goals. That will likely result in a non-linear path towards domination, lasting a long time and resulting in a high number of civilian causalities. The Syrian Democratic Forces are perceived to be YPG-dominated, which may provoke an armed resistance by the Arabs of Raqqa, especially in cases of brutal conduct against civilians conducted by the YPG. That scenario will slow the SDF’s advancement towards the South and will force it to prematurely withdraw leaving a power and governance vacuum behind. The rest of the American-supported groups, such as Maghawer al-Thawra, the Lions of Sharkia, Shahid Ahmed Abdou Brigades, and Ahmed al-Garba forces in al-Hassaka, are no more disciplined and will bring the same problems.
The situation for the Assad regime and Hizbullah might look brighter, but threats of American air attacks and Russia’s decision to refrain from a direct confrontation will neutralize this advantage. The rest of the regime-aligned forces will include the nascent groups working under the Fifth Corps, such as the tribal forces, whose capabilities are still questionable. The Russians bet on filling the vacuum in Dir Ezzor after the failure of the American-led forces to establish control. That gamble indicates that the battle will not be settled any time soon and its outcome is uncertain.
The distraction from the western fronts does not exclude them from the spot light. HTS (al-Nusra coalition) will try to expand geographically and attract more groups and individuals to its coalition in order to weaken the moderates’ body. That might be countered if the newly formed Turkish-led forces succeed in uniting all moderates under the Euphrates Shield zone and advances into Idlib. Other interesting events include the race to contact and empower the LACs in Idlib and northern Aleppo as a humanitarian and development player in a future political transition or a stable ceasefire. Europeans and Americans have been a strategic partner of the LACs, and now also the Russians are looking for a place in Idlib and other de-escalation zones. All powers will seek to improve the capacity and legitimacy of the LACs, but competing over the political alignment of the LACs is counterproductive. The use of LACs as political tools for any party will undermine their role as professional service providers and as a popular medium between the government and the local population.
Recommendations for the opposition and international players:
1- The political opposition: Starkly, there were no Syrian signatories to the agreement, neither the government nor the opposition. This suggests that Syrians have lost control over the trajectory of the war in their own country. In Astana, the Syrians are observers rather than participants in any discussions concerning their cause, a position in Astana that disregards them no less than in Geneva. It is of interest to all parties, except for the Assad regime and Iran, to support the opposition in both conference. For that, there is a need to increase the capacity and legitimacy of the delegations. This can be achieved through:
- Uniting the delegations of both Astana and Geneva in consultation with the opposition allies. Merging the military weight of the Astana delegation with the regional and international recognition of the Geneva delegation will make one solid front in both venues. This will not happen without a show of will from the two delegations and without some pressure on the allies—specifically Turkey and Saudi Arabia. These efforts entail recalibrating the current political and military establishments of the opposition in order to accommodate such overdue restructuring.
- Increasing the technical capabilities of the delegation. Ever since Geneva I meetings in 2012, the opposition has needed to boost its capacity to conduct negotiations with the regime regarding myriad issues from humanitarian coordination to security reform, from reconstruction to the return of refugees. It is a mistake to assume that a constitution and elections will dominate the discussions. For example, the current de-escalation zones agreement includes minute details on the observers’ mechanisms and the international force composition and mandate, which are often out of the ream of expertise of unspecialized military officers. The failure to provide such capabilities will lead the delegation to blindly agree to unfavorable terms or unwittingly refuse to sign potentially favorable agreements.
- Increasing the legitimacy of the united delegation. Two dilemmas face the Syrian delegations in both Astana and Geneva: one is weak communication with their wider constituencies inside and outside of Syria; the other is the disconnect among local actors in the opposition-controlled area.
- Communicate with Syrians inside and outside of Syria. There is a need to improve the level and means of communication with Syrians in general, and especially those who count as natural constituency inside and outside of Syria. Direct messages 1) before negotiation rounds to explain the goals, 2) during the negotiations to elaborate on the development, and 3) after the end of rounds to summarize and hint on the future steps. It is possible to lose the message when there are too many delegations, each claiming to represent the Syrian cause.
- Communication with local elements in Syria. The more local support the more legitimacy is secured in the eyes of the international community. In Astana, the militias represent power brokers on the ground, but they still cannot speak for other elements like local councils. Geneva talks represent political elements and regional clout where more players on the ground are excluded. The political body of the opposition is responsible for securing the physical needs of its constituency and representing its demands. The failure to play that role casts doubt on its legitimacy.
2- The military opposition: The political opposition might look incompetent and unrepresentative to Syrians on the ground who have made significant sacrifices, but without the opposition it would be doubtful to receive political acknowledgement from the international community and hence weaken the possibility to transform the military achievements of Syrians on the ground into an institutionalized political gain. The military factions have hard tasks as they are responsible for defending their territories, as well as supporting the political process at once. The overall weight of the Syrian opposition does not give room for more than one delegation. Therefore, we recommend the following:
- Pressuring to unite the negotiations delegation. The political opposition needs the militias’ help to coordinate the efforts and to lobby the allies in order to support merging the two delegations.
- Providing a vision for the militias’ role in the transition period and the future Syria. Specific answers about the militias’ willingness and ability to professionally deliver security during the transition period, disarmament conditions, and integration in one united Syrian Army are much needed. Without clear and detailed answers to these questions, the negotiations process will be harder and all of the opposition’s sacrifices will be wasted. That eventually will transform the discontented fighter into a ticking time bomb in the future.
3- The Local Councils: The LACs are an important Syrian asset for future stabilization and should be preserved at any cost. Therefore, we suggest the following:
- Focus on professionalism in delivering services indiscriminately to all Syrians regardless of their faith, gender, and ideology.
- Boost the LACs legitimacy by observing the elections cycles and avoid any political or ideological aligning.
- Assure transparency in all transactions with donors to avoid any side deals with any harmful regional or international coalitions in the future.
4- The US and the EU: Both entities can enhance the substance of the current negotiations in Astana and Geneva, as well as facilitate the institutional transition through the following:
- Stepping up the US and the EU involvement in Astana on the political and technical level to assure better agreements in terms of implementation and following-up mechanisms. That would make it harder to be ignored and will reemphasize the US and EU’s responsible position towards the Syrian cause.
- Supporting efforts to unite the Syrian delegations, both financially and technically. It is worth noting the importance of building a Syrian expertise base instead of the unsustainable reliance on costly and unproductive western consultancy companies.
- Respect the professional and neutral aspects of the LACs and avoid pushing them into a polarized regional and international muddy field.
5- Russia: There is a big room for Russia to reach quick and more effective results in resolving the conflict, improving the substance and outcome of the ongoing negotiations in Astana and Geneva, and facilitating the institutional transition through the following:
- Avoiding undermining the legitimacy of the opposition and show goodwill by not targeting their local constituencies and deterring the regime and the Iranians from the same. A strong and legitimate opposition can uphold the agreements and assure their implementation, while a weakened one is a guarantee for instability and prolonged war.
- Facilitating access of humanitarian aid to the opposition areas to build trust with Syrian citizens and also to support the legitimacy of the opposition in their eyes.
- Establishing a communication protocol with the opposition delegation to Astana and Geneva in order to improve the substance and outcome of the negotiation rounds. The opposition delegation should obtain all necessary information that enables it to effectively represent its cause and transform the outcome into concrete results.
- Respect the popular representation nature of the LACs and support their role as a professional service and security provider. Avoid any miscommunication that would result in delegitimizing them in the eyes of their constituency or their main sponsors. Russia can be a positive force to bring stability into the opposition areas by securing an environment conducive to the return of refugees and the reconstruction of infrastructure.
- Cooperate with European countries and the US on supporting the LACS. This can be a good venue for trust-building and de-escalation between the US and Russia in Syria.